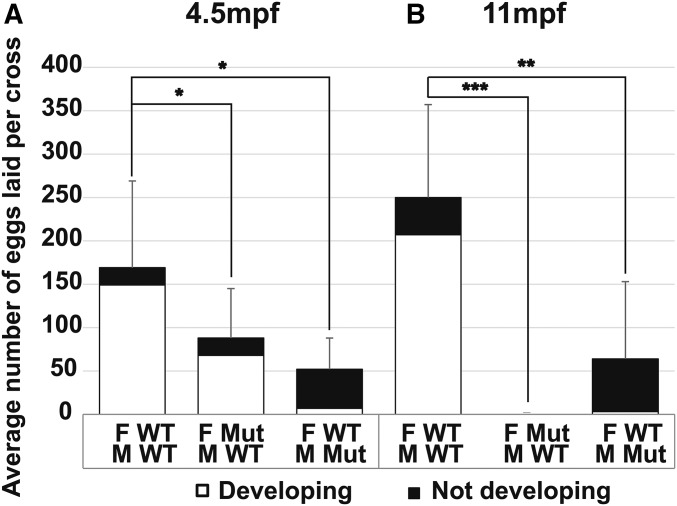
Figure 2.
Fertility tests for adult amh mutants and wild types. (A) Average number of eggs laid per cross from wild-type females crossed to wild-type males (11 crosses), amh-26 mutant females crossed to wild-type males (11 crosses), and wild-type females crossed to amh-26 mutant males (4 crosses) at 4.5 mpf. (B) Average number of eggs laid per cross from wild-type females crossed to wild-type males (8 crosses), amh-26 mutant females crossed to wild-type males (7 crosses), and wild-type females crossed to amh-26 mutant males (6 crosses) at 11 mpf. For each cross, one individual female (either mutant or wild-type sibling) was paired with three nonsibling wild-type males, or for the reciprocal test, one individual male (either mutant or wild-type sibling) was paired with three nonsibling wild-type females. Eggs were collected and counted at 1 dpf and 3 dpf; embryos were scored as developing normally (white bars), or as not developing or improperly developing (black bars). Statistical significance: * 0.05 < P < 0.01, ** 0.01 < P < 0.001, and *** P < 0.001, Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Error bars show SD. F, female; M, male; Mut, mutant; WT, wild type.