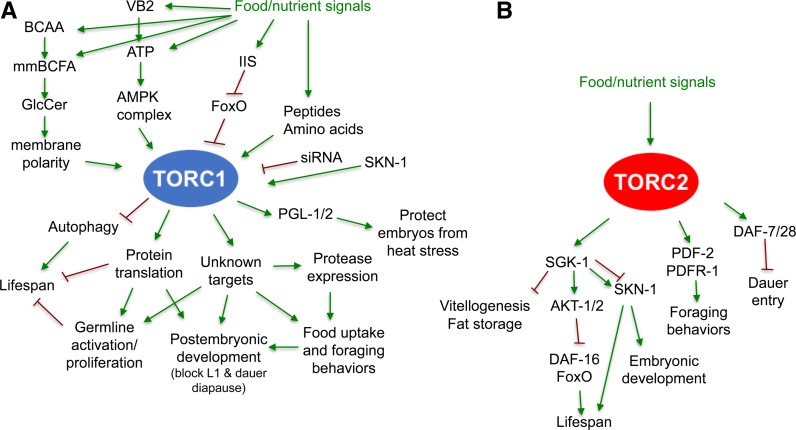
Figure 2.
Abbreviated illustration of pathways, or cellular processes, identified to act upstream or downstream of TORC1 (A) and TORC2 (B) in C. elegans. These models are based mainly upon genetic analyses but also incorporate mechanistic findings from other systems. In many cases, C. elegans researchers analyzed the TORC1 or TORC2 function under starvation or dietary restriction conditions, when food/nutrient signals were absent or reduced. Arrows indicate the positive regulation or input, whereas T-bars indicate negative regulation, with neither necessarily indicating direct regulation. Please see the text for more discussion on these pathways and downstream physiological functions. TOR functions are notably complex and wide ranging, extending beyond the canonical functions that have been identified in other organisms. For example, the stress response transcription factor SKN-1 has three different roles regarding the two TOR complexes: it promotes transcription of several TORC1 components, its target genes are activated when TORC1 or translation is inhibited, and it is regulated downstream of TORC2 (see sections Roles of TORC2 in regulating development and behaviors and Life span extension and increased stress resistance from TORC1 inhibition). BCAA, branched-chain AAs; GlcCer, glycosylceramide; IIS, insulin/IGF signaling; mmBCFA, monomethyl branched-chain fatty acid; TOR, Target of Rapamycin; TORC, TOR Complex; VB2, vitamin B2.