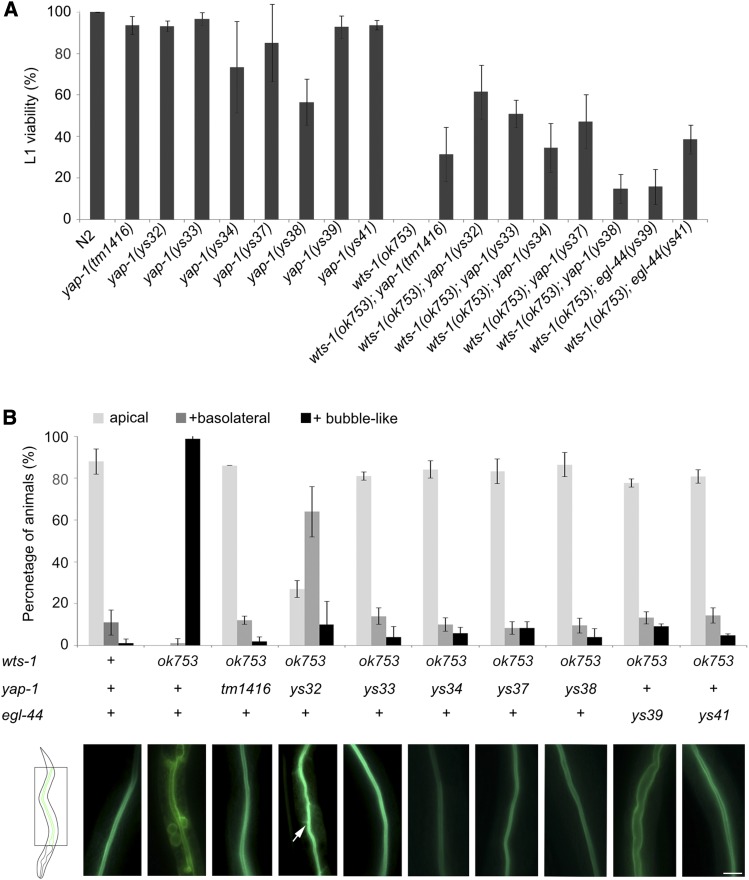
Figure 2.
Mutations in yap-1 or egl-44 suppress wts-1 mutant phenotypes (A) Results of phenotypic analyses of wts-1, yap-1, egl-44, wts-1; yap-1, wts-1; egl-44 mutant worms. L1 viability is calculated as the ratio of the number of adult worms to total number of hatched L1 worms. (B) GFP::ACT-5 localization in the wild type N2, wts-1 mutant, and double mutant with wts-1 and various alleles of yap-1 or egl-44. Upper panel: “+ basolateral” = worms that showed apical and basolateral localization of the protein; “+ bubble-like” = worms that had proteins localized in bubble-like structures, in addition to the apical and basolateral sides. Two days after hatching, ACT-5 localization was measured. At the time of observation, wts-1 mutants were arrested at the L1 stage. The wild type, wts-1; yap-1, and wts-1; egl-44 worms were at the L4 stage. Lower panel: representative images of GFP::ACT-5 distribution in each genotype of the worms. Arrow: laterally localized GFP::ACT-5. Data: average percentages of worms SD Bar, 10 μm.