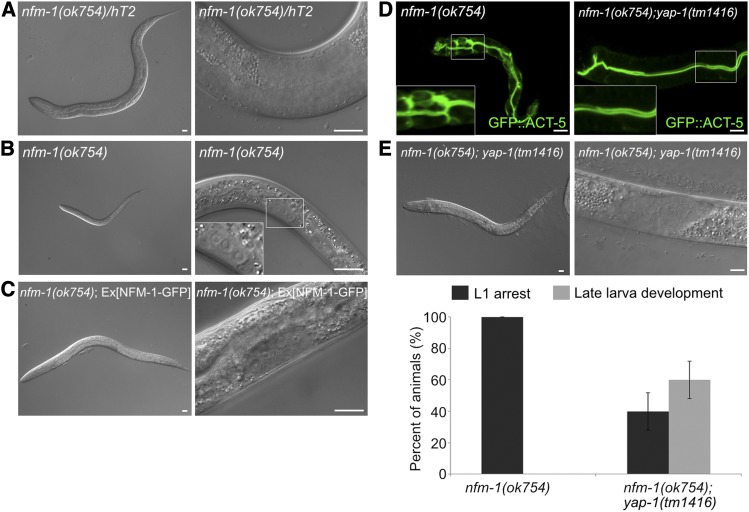
Figure 6.
yap-1 suppresses polarity defects and larval lethality of the nfm-1 lacking mutant (A and B) Representative images of 3-day-old larvae of (A) nfm-1 heterozygous mutants and (B) nfm-1 homozygous mutants. nfm-1 homozygous mutants were arrested in the L1 stage, whereas heterozygous mutants developed to the L4 stage. Boxed region: magnification of somatic gonad precursor cells. (C) Rescue with wild-type copies of NFM-1 allowed only L3 development, possibly due to the germline defect in nfm-1(ok754). (D) Suppression of polarity defects in nfm-1(ok754) by introduction of yap-1 mutation. (E) Suppression of early larval arrest phenotype of nfm-1(ok754) by yap-1. yap-1 mutation also allowed only L3 development of nfm-1(ok754). Lower graph: average percentage of worms ± SD. Bar, 10 μm.