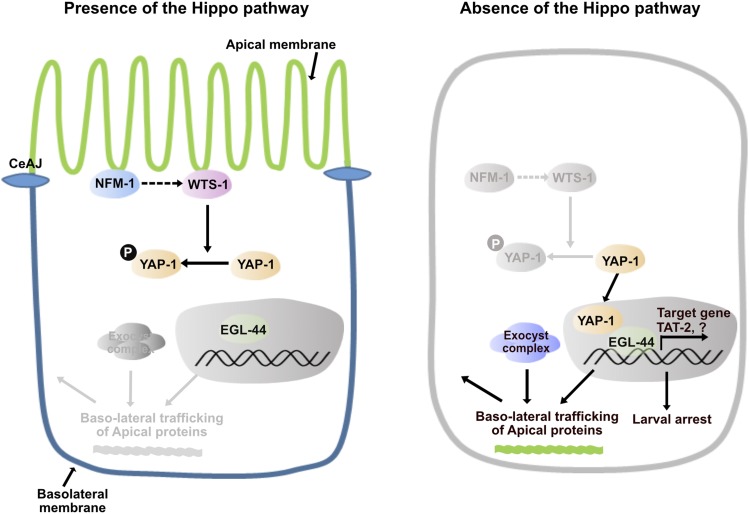
Figure 7.
The working model of the Hippo pathway in the cellular polarity maintenance based on our genetic studies After the C. elegans adherens junction (CeAJ) forms, WTS-1 is localized to the subapical membrane, possibly in a manner that depends on NFM-1, and may be activated. Activated WTS-1 phosphorylates YAP-1 and inhibits its nuclear localization. In the nucleus, EGL-44 alone cannot induce expression of its target genes. In the absence of the Hippo pathway (e.g., in nfm-1, wts-1 mutants), YAP-1 entry to the nucleus, and interaction of YAP-1 with EGL-44, are not restricted. YAP-1-EGL-44 ectopically induces target gene expression, including TAT-2. Misregulated target genes may influence the identities of the plasma membrane domain; consequently, polarized sorting of newly produced proteins to the distinct domain is abrogated. Exocytosis-mediated abnormal sorting of apical proteins such as ACT-5 to the basolateral region leads to disintegration of intestinal membranes and organismal death.