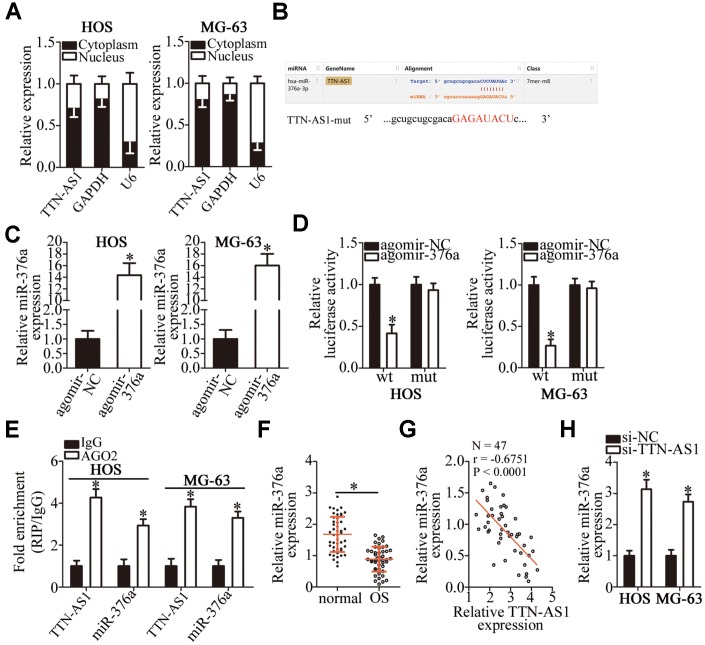
Figure 3.
TTN-AS1 functions as a ceRNA for miR-376a in OS cells. (A) The distribution of TTN-AS1 within OS cells was determined by the nuclear/cytoplasmic fractionation assay. (B) The wild-type miR-376a-binding sequences in TTN-AS1, as predicted by starBase 3.0. The mutations in the TTN-AS1 sequence that disrupt the interaction between TTN-AS1 and miR-376a are shown too. (C) HOS and MG-63 cells that were transfected with either agomir-376a or agomir-NC were harvested and analyzed for miR-376a expression by RT-qPCR. *P < 0.05 vs. the agomir-NC group. (D) Luciferase reporter assays were performed on HOS and MG-63 cells that were transfected with either agomir-376a or agomir-NC and either TTN-AS1-wt or TTN-AS1-mut. *P < 0.05 vs. group agomir-NC. (E) The RIP assay was conducted to assess the direct interaction between TTN-AS1 and miR-376a. *P < 0.05 vs. the IgG group. (F) The expression profile of miR-376a in the 47 pairs of OS tissues and adjacent-normal-bone tissue samples was analyzed by RT-qPCR. *P < 0.05 vs. the normal bone tissues. (G) An inverse correlation between TTN-AS1 and miR-376a expression levels was validated in the OS tissue samples by Spearman’s correlation analysis. r = -0.6751, P < 0.0001. (H) Expression of miR-376a in HOS and MG-63 cells transfected with either si-TTN-AS1 or si-NC was determined by RT-qPCR. *P < 0.05 vs. the si-NC group.