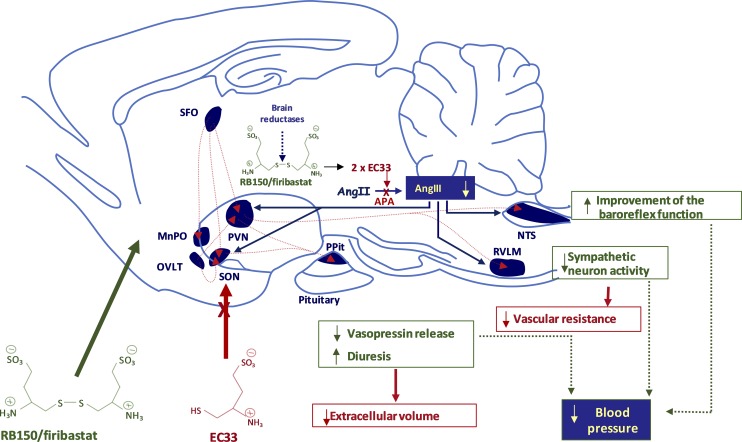
Fig. 7.
Mode of action of the APA inhibitor prodrug RB150/firibastat on the control of blood pressure in hypertensive rats. After oral administration, the disulfide bridge enables RB150 to cross the blood–brain barrier and to enter the brain. At the opposite, EC33 is not able to enter the brain. In the brain, the disulfide bridge of RB150 is cleaved by brain reductases generating two active molecules of EC33. EC33 subsequently inhibits brain APA activity and blocks the formation of brain Ang III, known to exert, in brain structures (PVN, SON, PPit, NTS, and RVLM), a stimulatory action on the control of blood pressure in hypertensive rats. This results in a blood pressure decrease via a decrease in arginine-vasopressin release and sympathetic neuron activity and an improvement of the baroreflex function. The red dashed lines represent the neuronal angiotensinergic pathways in the adult rat brain. MnPO, median preoptic nucleus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; OVLT, organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis; PPit, posterior pituitary; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; RVLM, rostral ventrolateral medulla; SFO, subfornical organ; SON, supraoptic nucleus.