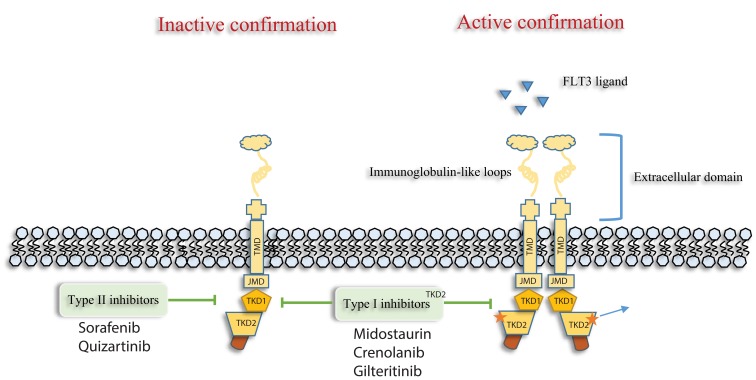
Figure 1.
Type I FLT3 inhibitors (Midostaurin, Gilteritinib and crenolanib) bind the FLT3 receptor in the active as well as inactive conformation, while Type II FLT3 inhibitors (Sorafenib, Quizartinib) bind the FLT3 receptor in the inactive conformation. As a result of this affinity, type I acts on both FLT3-ITD and TKD mutations, whereas type II act only on FLT3-ITD. Abbreviations: FLT3, FMS-like tyrosine kinase; TMD, transmembrane domain; JMD, juxtamembrane domain; TKD, tyrosine kinase domain.