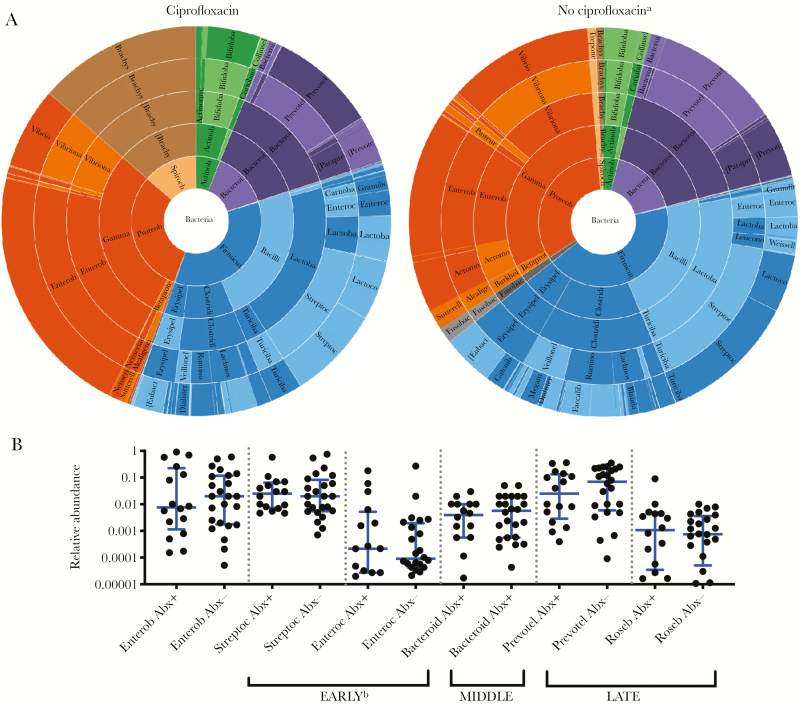
Figure 4.
Ciprofloxacin is associated with minimal microbiota changes. A, Comparison of stool samples from patients with cholera in which ciprofloxacin was or was not detected; samples with phage or trace antibiotic detection were removed. P = .158, by permutational multivariate analysis of variance (Bray-Curtis dissimilarities). Brachyspira species are in brown. B, Relative abundance of taxa previously shown to be associated with early, middle, and late phases of recovery from cholera, with (Abx+) and without (Abx-) antibiotic detection. No significant differences were detected by the Mann-Whitney U test (α = 0.05). P values were adjusted for multiple comparisons. Bars and whiskers denote medians and interquartile ranges, respectively. Analyses were restricted to samples without detection of trace antibiotic and phages. See Supplementary Table 2 for further details. Bacteroid, Bacteroides; Enterob, Enterobacteriaceae (family); Enteroc, Enterococci; Prevotel, Prevotella; Roseb, Roseburia; Streptoc, Streptococci. aSamples negative for ciprofloxacin were also negative for metronidazole. bEnterobacteriaceae is grouped with genera associated with the early phase of recovery because the family contains Escherichia, which is known to be associated with this phase.