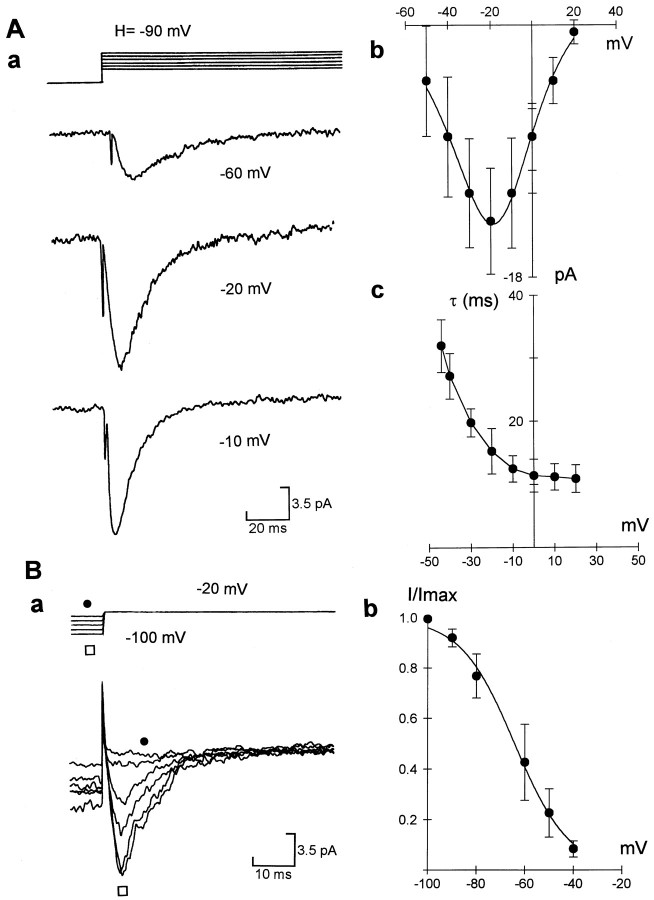
Fig. 1.
Kinetic characteristics of T-type channel currents in cell-attached patches. Aa, T-type currents were elicited by steps of +10 mV from a holding potential of −90 mV; representative traces were elicited by steps to −60, −20, and −10 mV, respectively. Ab, Current–voltage relation of T-type currents (n = 5). Solid lineis the best fit of the product of the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation and Boltzmann equation (cf. Dale, 1995). Ac, Graph showing time constant of inactivation of T-type currents versus test voltage in four cells. Ba, T-type currents were elicited by steps to −20 mV from holding potential varied from −100 to −40 mV.Bb, Steady-state inactivation of T-type currents.Solid line is the best fit of Boltzmann relation,I = {1 + exp[(V +V1/2)/k]−1}−1, where V1/2 = −62 ± 6.3 mV, andk = 11.6 ± 3.2 (n = 4). Error bars represent SEM in this and all figures unless stated otherwise.