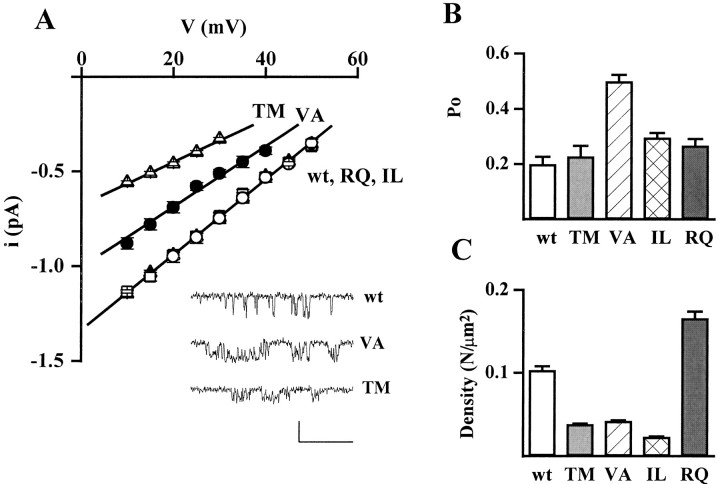
Fig. 3.
Effect of FHM mutations on single-channel current and conductance, open probability, and density of functional channels. Cell-attached patch-clamp recordings as in Figure 2. A, Unitary current–voltage,i–v, relationships of calcium channels containing wt and mutant human α1A-2 subunits. Unitary current values of wt (○), TM (▵), VA (•), IL (■), and RQ (▴) channels are averages from 8, 7, 9, 8, and 14 patches, respectively. For each patch, values of i at a given voltage are averages of many measurements on well resolved openings (compare insetshowing unitary activity at +20 mV on an expanded time scale; calibration: 40 msec, 1 pA). The values of i refer to the prevailing larger current level shown in the inset, which was much more frequently occupied with respect to other short-lived subconductance levels (particularly present in the VA mutant). The slope conductances of the average i–vrelationships are 20 pS for wt, IL, and RQ; 16 pS for VA; and 11 pS for TM. B, Open probability,po, at +30 mV of calcium channels containing wt and mutant human α1A-2 subunits. Averagepo values were obtained from the same patches from which the average i–v relationships were derived (n = 8, 7, 9, 8, and 14 patches for wt, TM, VA, IL, and RQ, respectively). The very similar average values of i for wt, RQ, and IL assure that the relatively small difference between the averagepo values of the three channels are not caused by any artifactual difference of voltage across the patches. All the patches contained only one channel. For each patch,po values were obtained by averaging the open probabilities measured in each sweep in segments with activity (n = 10–180). Statistical significance of differences with respect to wt: p ≪ 0.0001 for VA;p < 0.01 for IL; and p < 0.08 for RQ. C, Density of functional calcium channels containing wt and mutant human α1A-2 subunits. The density of functional channels was calculated from the average number of channel per patch and the average patch area in 144, 299, 192, 73, and 193 cell-attached patches on cells transfected with wt, TM, IL, RQ, and VA subunits, respectively. The average number of channel per patch in cells transfected with wt, TM, IL, RQ, and VA subunits was 0.98, 0.40, 0.30, 1.45, and 0.47, respectively. The corresponding average pipette resistance was 1.59 ± 0.09, 1.35 ± 0.05, 1.04 ± 0.03, 1.68 ± 0.08, and 1.29 ± 0.04 MΩ, respectively.