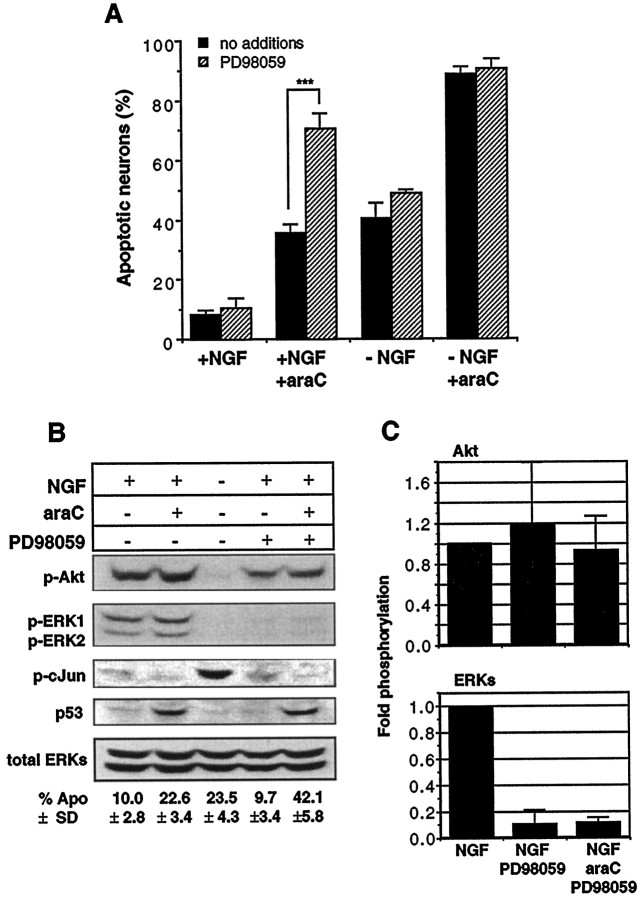
Fig. 7.
Suppression of ERK activity by PD98059 renders neurons more susceptible to araC: a comparison of signaling pathways.A, Neurons were cultured in the presence or absence of NGF (20 ng/ml), araC (100 μm), or PD98059 (50 μm) for 14 hr in the indicated conditions before being fixed, stained, and counted. All media contained 0.2% DMSO. Results shown are the mean ± SEM of three to five independent experiments (**p < 0.002; Student’s t test). See Figure 8 for photomicrographs of apoptotic nuclei.B, Neurons were treated with 20 ng/ml NGF (lanes 1, 2, 4, 5), 100 μm araC (lanes 2, 5), and 50 μm PD98059 (lanes 4, 5) for 12 hr and then processed for immunoblotting as in Materials and Methods. The panels show the results of probing with the following antibodies (top to bottom): anti-phospho-Akt (serine 473), anti-phospho-ERK1/2, anti-phospho-c-Jun (serine 63), anti-p53, and anti-ERK1/2. Results shown are representative of three independent experiments, except for anti-phospho-Akt and anti-phospho-c-Jun, which are representative of two independent experiments. The numbers below the lanes indicate the percentage of apoptosis and are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.C, Fold-phosphorylation as determined by optical densitometry (see Materials and Methods): top panel, phospho-Akt (n = 2); bottom panel, phospho-ERKs (n = 3); both normalized to total ERK. Error bars represent the SD and range for ERK and Akt, respectively.