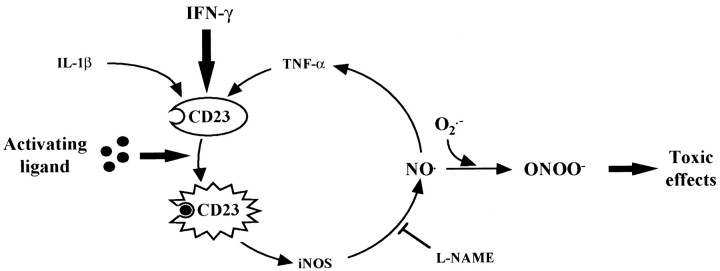
Fig. 7.
Schematic representation of CD23-mediated iNOS induction and TNF-α production pathway in glial cells. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-γ, induce the expression of CD23 in glial cells. This effect is potentiated by TNF-α and IL-1β. Triggering of CD23 antigen by an appropriate ligand results in iNOS induction and the subsequent release of NO, which in turn upregulates the production of TNF-α. The NOS inhibitor l-NAME completely inhibits the production of both NO and TNF-α in vitro. This pathways results in an auto-amplification of NO production, which could reach a toxic threshold. NO toxicity would in part involve the formation of peroxynitrite, which has been shown to initiate lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation and inactivation. All of these events could contribute to the death of dopaminergic neurons in PD.