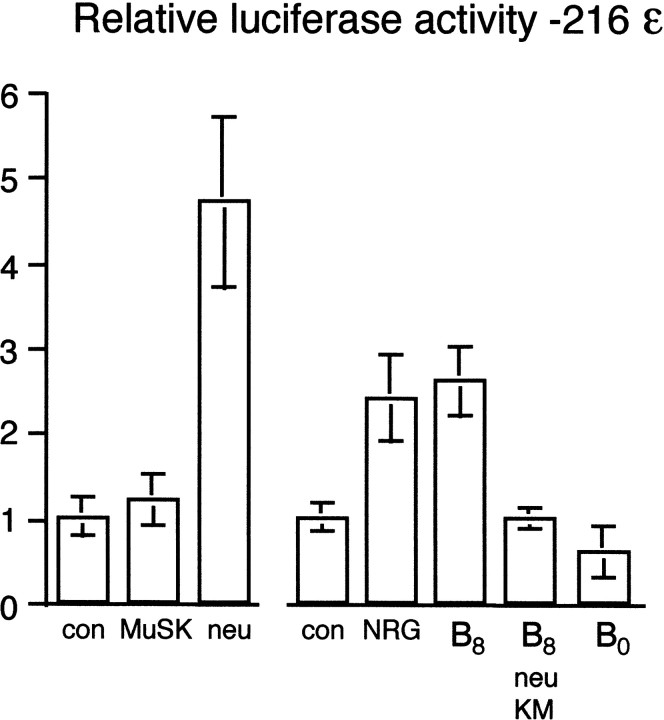
Fig. 7.
MuSK does not directly increase transcription of the AChR-ε subunit gene in C2C12 myotubes. The transcriptional activity of the MuSK and erbB2/neu kinase domains was directly compared by culturing C2C12 myoblasts on a laminin substrate. Myoblasts were transfected with either pLCF216ε (control: con) or pLCF216ε with pMuSKneuTMuSK_myc (MuSK) or pMuSKneuTneu_myc (neu), a chimeric receptor that included the erbB2/neu kinase domain. The role of MuSK in AChR transcription was investigated further by culturing C2C12 myoblasts on a substrate of neural mini-agrin cN257C21B8adhered to laminin (B8). The requirement for erbB2/neu was tested by cotransfecting a dominant-negative erbB2/neu mutant into myoblasts similarly cultured on a laminin/cN257C21B8 substrate (B8, neu KM). Mini-agrin cN257C21B0 (B0), which does not phosphorylate MuSK or induce AChR clustering, did not increase transcription. Also shown is the transcriptional activity of a saturating amount of soluble NRG (NRG).