Fig. 2.
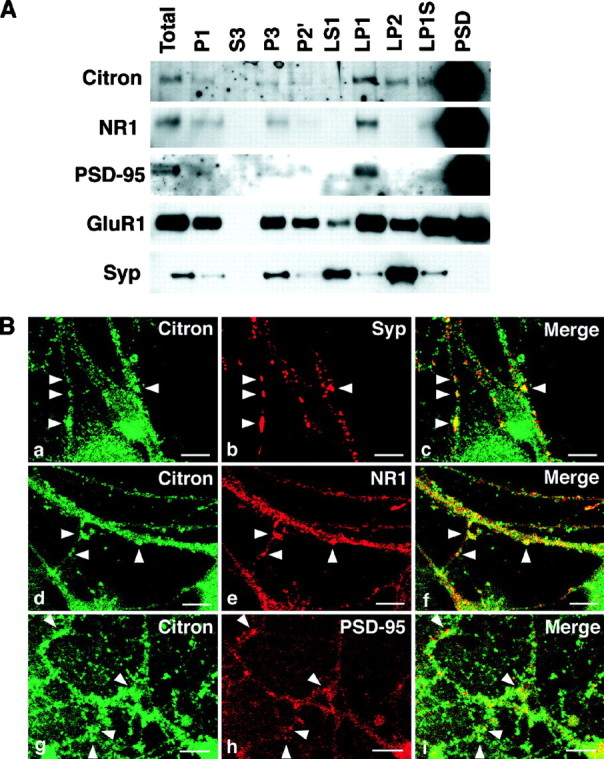
Citron and PSD-95 cofractionate into the PSD fraction and are colocalized at thalamic glutamatergic synapses.A, Biochemical fractionation (See Materials and Methods for the definition of each fraction) reveals that Citron is highly enriched into the PSD fraction, along with NR1 and PSD-95. A similar amount (1 μg) of proteins was loaded in each lane. Citron is detected in the total homogenate (Total) and P1 fraction (P1) but not in the cytosolic fraction (S3). Citron is expressed in most membrane fractions but is more concentrated in the synaptic membrane fraction (LP1) than in the microsomal membranes (P3). Although slightly detected in the synaptic vesicle fraction (LP2), a predominant amount of Citron is found in the PSD fraction (PSD). B,a–c, Colocalization between Citron and synaptophysin, a presynaptic vesicle marker; d–f, colocalization between Citron and NR1; g–i, colocalization between Citron and PSD-95. Typical puncta showing a colocalization are illustrated byarrowheads. Note that the Citron puncta only partially overlap with the synaptophysin (Syp)-, NR1-, or PSD-95-positive puncta. Occasionally, a spinehead-like structure was visualized using anti-Citron antibodies. Scale bars, 10 μm.
