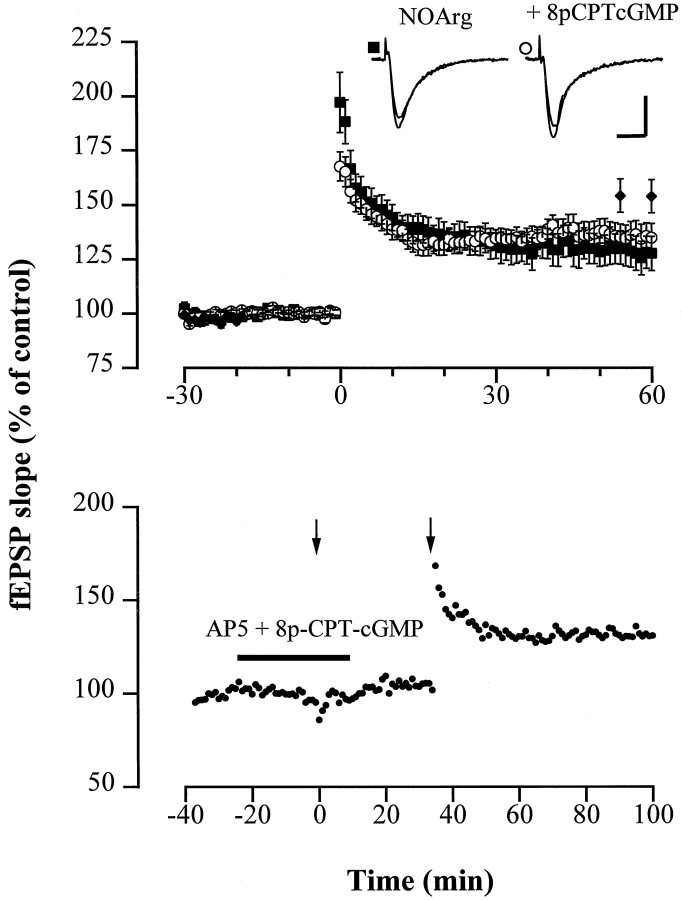
Fig. 7.
The membrane-permeable cGMP analog 8p-CPT-cGMP fails to abolish suppression of LTP by the NOS inhibitor NOArg and the NMDA receptor antagonist AP-5. A, Average potentiation of the fEPSP slope after theta burst stimulation in slices from WT mice treated with 100 μm NOArg (▪; n = 13) and 100 μm NOArg plus 50 μm 8p-CPT-cGMP (○; n = 10), respectively. For comparison, the fEPSP slope in the control (normal ACSF) 55 and 60 min after tetanus is shown (♦; n = 12). The mean baseline slope (pretetanus control) was −0.34 ± 0.03 and −0.27 ± 0.03 mV/msec in slices bathed in ACSF containing NOArg and NOArg plus 8p-CPT-cGMP, respectively. Inset shows representative fEPSP recordings. Calibration: 10 msec, 1 mV. B, Typical example of an fEPSP recording in a hippocampal slice; the theta burst stimulation (left arrow) failed to induce detectable LTP in the presence of AP-5 (50 μm) and 8-pCPT-cGMP but induced significant potentiation of fEPSPs after wash-out of the compounds (right arrow), demonstrating the functional integrity of the preparation. The mean baseline slope was −0.27 ± 0.03 mV/msec.