Fig. 4.
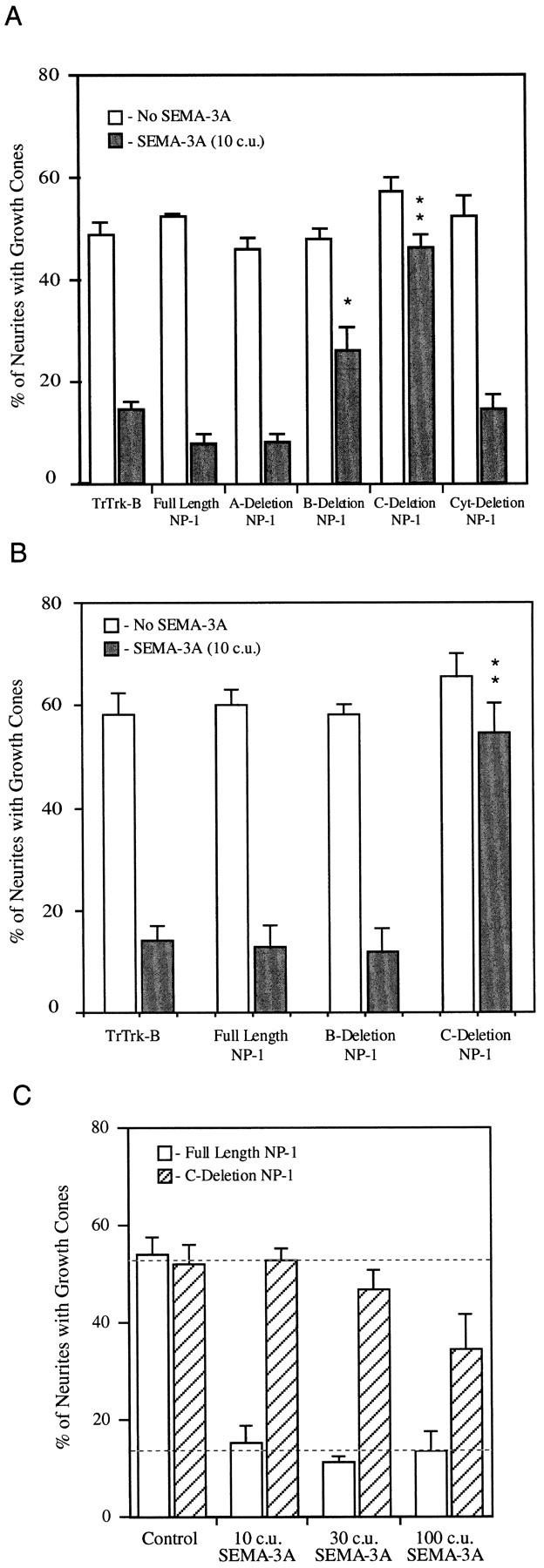
C-deletion neuropilin-1 is a dominant negative receptor component for SEMA-3A. Sympathetic neurons were transfected with the indicated constructs and then exposed to either control media or media containing AP-SEMA-3A. After 35 min, the cultures were fixed, and the percentage of myc-labeled neurites with growth cones were counted. A, The addition of 10 c.u. of AP-SEMA-3A induces collapse in growth cones expressing truncated Trk-B, full length neuropilin-1, and cytoplasmic-deletion neuropilin-1. Growth cones expressing C-deletion neuropilin-1 do not respond to SEMA-3A. Expression of B-deletion neuropilin-1 caused a partial block of SEMA-3A-induced collapse. B, Sympathetic neurons were transfected with test constructs and then reaggregated. Growth cones expressing truncated Trk-B, full-length neuropilin-1, and B-deletion neuropilin-1 all collapse in response to AP-SEMA-3A. Growth cones expressing C-deletion neuropilin-1 do not respond to SEMA-3A. The SEM of three to eight experiments is shown for each condition. *p ≤ 0.01; **p ≤ 0.001 by Student’s two-tailed t test. C, Sympathetic neurons were transfected with either full-length or C-deletion neuropilin-1 and then reaggregated. Ten, 30, or 100 c.u. of SEMA-3A induced growth cone collapse in neuropilin-1-transfected neurons. Neurons transfected with C-deletion neuropilin-1 did not respond to 10 or 30 c.u. of AP-SEMA-3A and were partially responsive at 100 c.u. The concentration of SEMA-3A required to induce 50% collapse of sympathetic neurons was shifted to ∼100-fold higher concentrations by C-deletion neuropilin-1.
