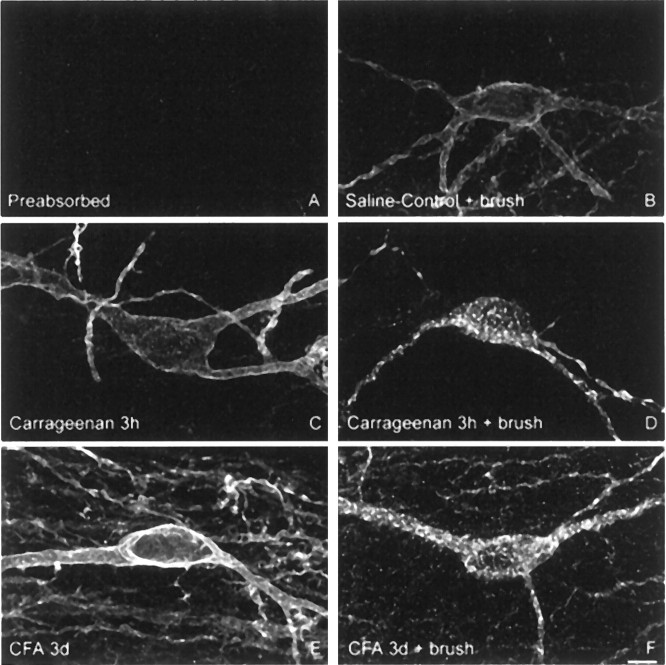
Fig. 2.
Normally innocuous mechanical stimulation induces SPR internalization in lamina I SPR-expressing neurons in carrageenan- and CFA-induced inflammatory pain but not in saline-injected animals. Confocal images of lamina I SPR-IR neurons ipsilateral to the injection of (B) saline, (D) carrageenan (3 hr), and (F) CFA (3 d), observed after innocuous mechanical stimulation. A is a preabsorbed control for SPR primary antibody, showing the specificity of the primary antibody against SPR. C andE present the basal SPR immunoreactivity observed after carrageenan (3 hr) and CFA (3 d) injections, respectively. Note that innocuous mechanical stimulation does not induce any SPR internalization in saline-injected animals, whereas this same stimulus induces SPR internalization in CFA- (F) and carrageenan-injected (D) rats. Note also the increase in immunofluorescence level in lamina I neurons after CFA injection (E), whereas no changes are observed after carrageenan injection. These images, obtained from 60-μm-thick tissue sections, are projected from 18 optical sections acquired at 0.8 μm intervals with a 60× lens. Scale bar, 5 μm.