Fig. 4.
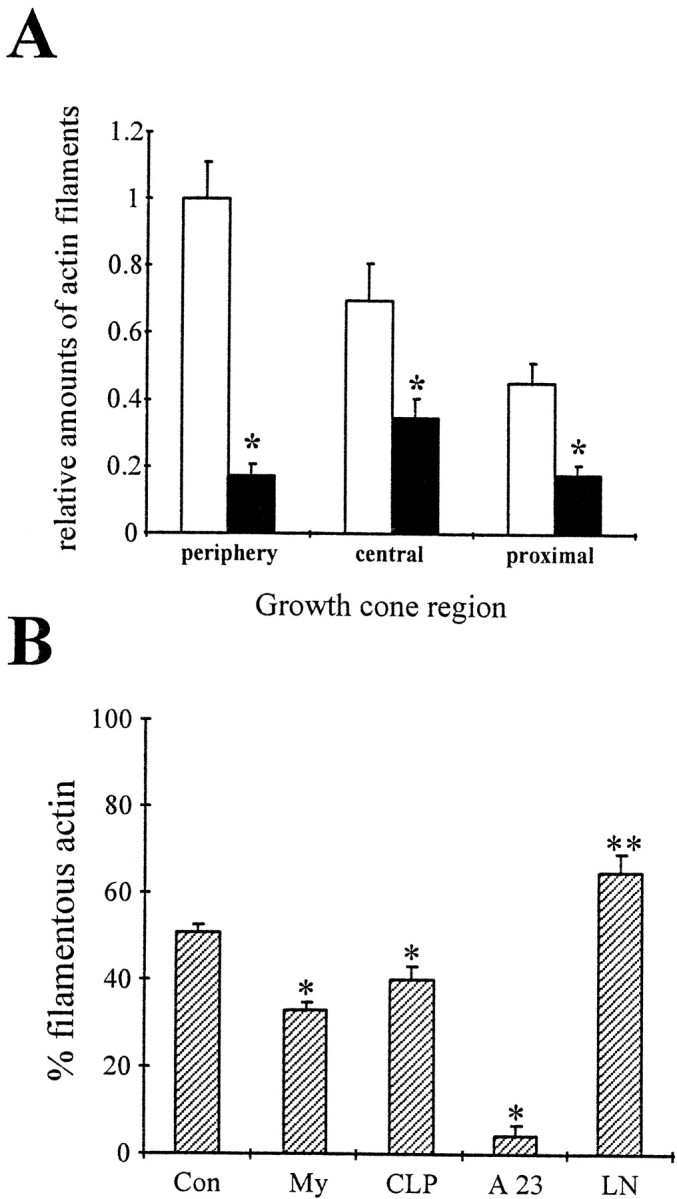
CNS myelin-associated growth inhibitors signal a disassembly of actin filaments. A, Motor neurons were grown on FN for 2 d, treated with PBS (open bars) or 100 μg/ml CNS myelin (filled bars), and actin filaments were visualized with rhodamine-labeled phalloidin. Growth cones were divided into a peripheral region, a central region defined by intense microtubule staining, and 15 μm of the proximal neurite. Images were acquired using identical parameters, and the total fluorescence intensity was analyzed in each growth cone region on a pixel-by-pixel basis after background subtraction. All values were normalized to the total fluorescence intensity of the peripheral region in control growth cones. CNS myelin caused a significant reduction of rhodamine fluorescence in the peripheral region (*p< 0.001) and also in the central region (*p < 0.001) and the proximal neurite (*p < 0.001). The loss of rhodamine fluorescence suggests a net disassembly of actin filaments signaled by CNS myelin as reported for collapsin-1 (Fan et al., 1993). B, Freshly prepared, intact growth cone particles were incubated with 100 μg/ml CNS myelin (My), 15 μg/ml enriched collapsin-1 (CLP), a mixture of 2 mm CaCl2and 10 μm A23187 (A23), 50 μg/ml laminin (LN), or PBS (Con). After 1 hr, samples were solubilized and separated into a cytoskeletal fraction and cytosol fraction by high-speed centrifugation (100,000 ×gmax). Proteins were separated on 10% SDS-PAGE and blotted onto PVDF membranes. The percentage of total actin in each fraction was determined by densitometry. Plotted is the percentage of total actin immunoreactivity in the cytoskeletal fraction, most likely actin filaments of various lengths, for each treatment. A significant decrease in filamentous actin occurred during incubation with CNS myelin (*p < 0.0001) or enriched collapsin-1 (*p < 0.01). As our control, large increases in the free intracellular Ca2+concentration results in an almost complete depletion of actin filaments (*p < 0.0001). In contrast, incubation with LN caused an increase in actin immunoreactivity in the cytoskeletal fraction, suggesting a net polymerization of actin filaments (**p < 0.01).
