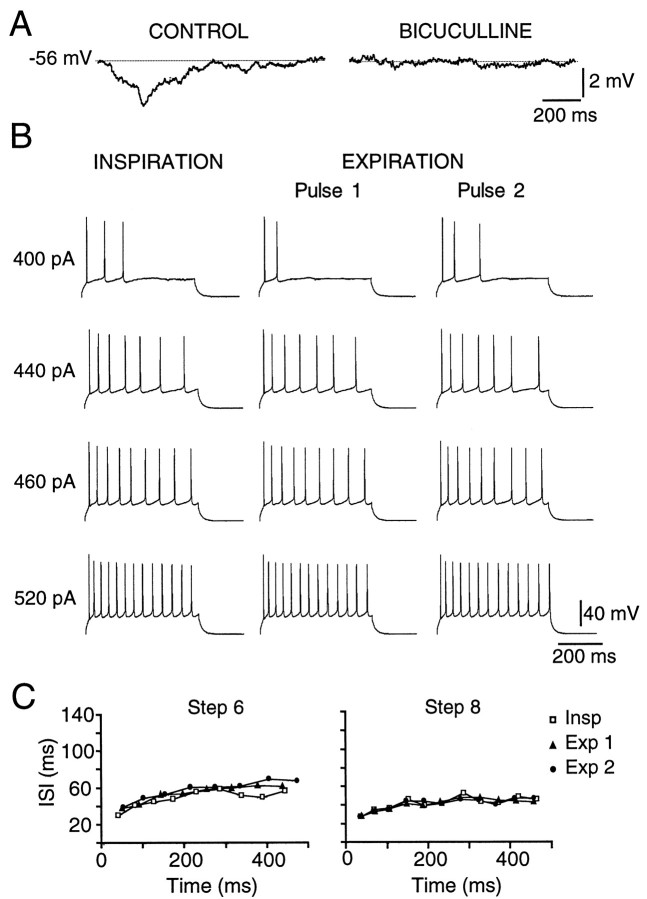
Fig. 4.
The hyperpolarizing inspiratory inhibition of PMNs and the reduction in PMN firing during inspiration are blocked by bicuculline. A, The same cell as in Figure3A at −56 mV. The membrane potential of a PMN during the inspiratory phase, before (CONTROL) and after local application of 200 μm bicuculline (BICUCULLINE). Traces are averages of eight inspiratory cycles. B, Bicuculline (200 μm) blocked the reduction in spike output during inspiration relative to expiration (same cell as in Fig. 2A). C, Bicuculline also blocked the increases in inspiratory interspike interval (same cell and current steps as in Fig.2E).