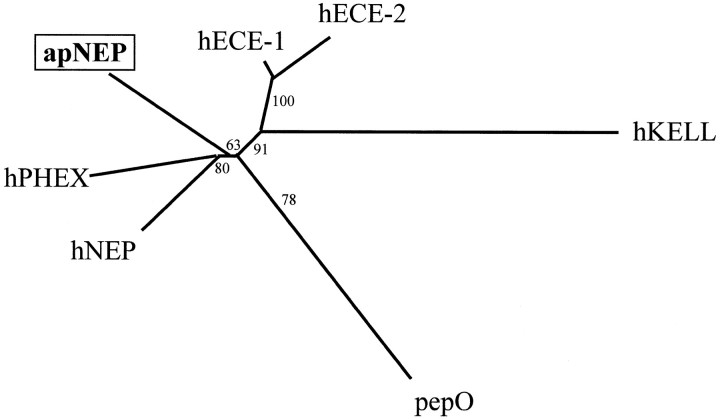
Fig. 11.
Phylogenetic analysis of the members of the NEP-like family. Sequences were aligned using the Clustal V program (Thompson et al., 1994). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Neighbor Joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987) with a bootstrap analysis that calculates the probability of occurrence of the presented branching for 100 possible trees (Felsenstein, 1993).hNEP, Human neutral endopeptidase (accession numberM26605); hECE-1, human endothelin-converting enzyme 1 (accession number Z35307); hECE-2, human endothelin-converting enzyme 2 (accession number AB011179);apNEP, A. californica neutral endopeptidase (accession number AF104361); hPHEX, human phosphate-regulating gene with homologies to endopeptidases on the X-chromosome (accession number Y10196); hKELL, human kell blood group protein (accession number M64934);pepO, lactococcus lactis PepO gene (accession number L04938). Sequences were aligned, and only the peptide regions that could be aligned with the PepO sequence were retained for the analysis; this roughly corresponds to the extracellular parts of the human and mollusk enzymes.