Fig. 1.
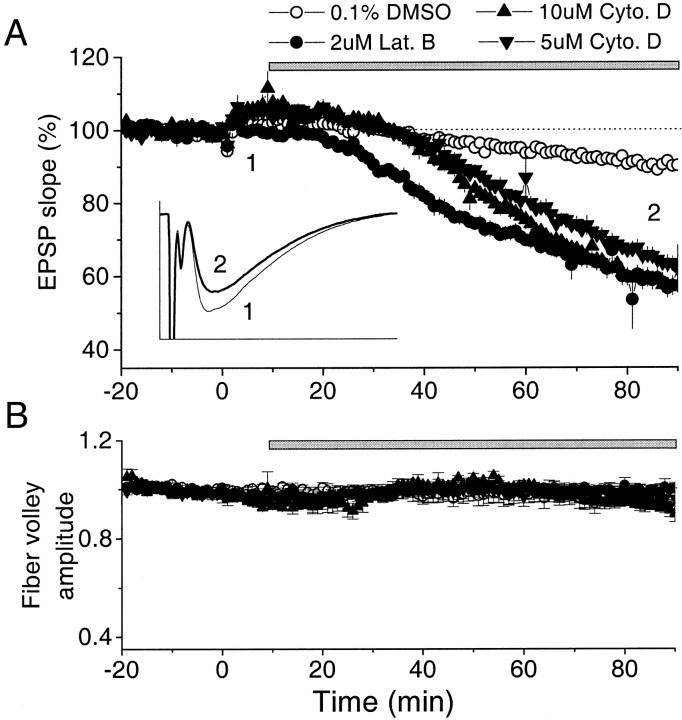
Bath-applied latrunculin B and cytochalasin D decrease fEPSP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice. A, Actin polymerization inhibitors latrunculin B (2 μm;n = 7) or cytochalasin D (5 μm;n = 7; 10 μm; n = 4) were applied extracellularly dissolved in 0.1% DMSO. Control solution contained 0.1% DMSO (n = 10). Thebar indicates the period of drug application. The average fEPSP in the DMSO controls, 2 μm latrunculin B, and 5 μm and 10 μm cytochalasin D experiments, measured at 70–80 min after its application, were 91, 59, 63, and 57% of the baseline, respectively. The small rise at time 0 occurred because LTP was induced in a different pathway.Inset, Examples of average traces before (thin line, 1) and after 2 μm latrunculin B application (thick line,2). Calibration: 2.5 mV, 25 msec. B, Effect of bath-applied APIs on fiber volley amplitude. The same symbols were used as in A. The effect on the amplitude of fiber volley of 0.1% DMSO ACSF (n = 7), 2 μm latrunculin B (n = 7), and cytochalasin D (5 μm; n = 7; 10 μm; n = 4) were indistinguishable, indicating no effect of APIs on presynaptic excitability.