Fig. 5.
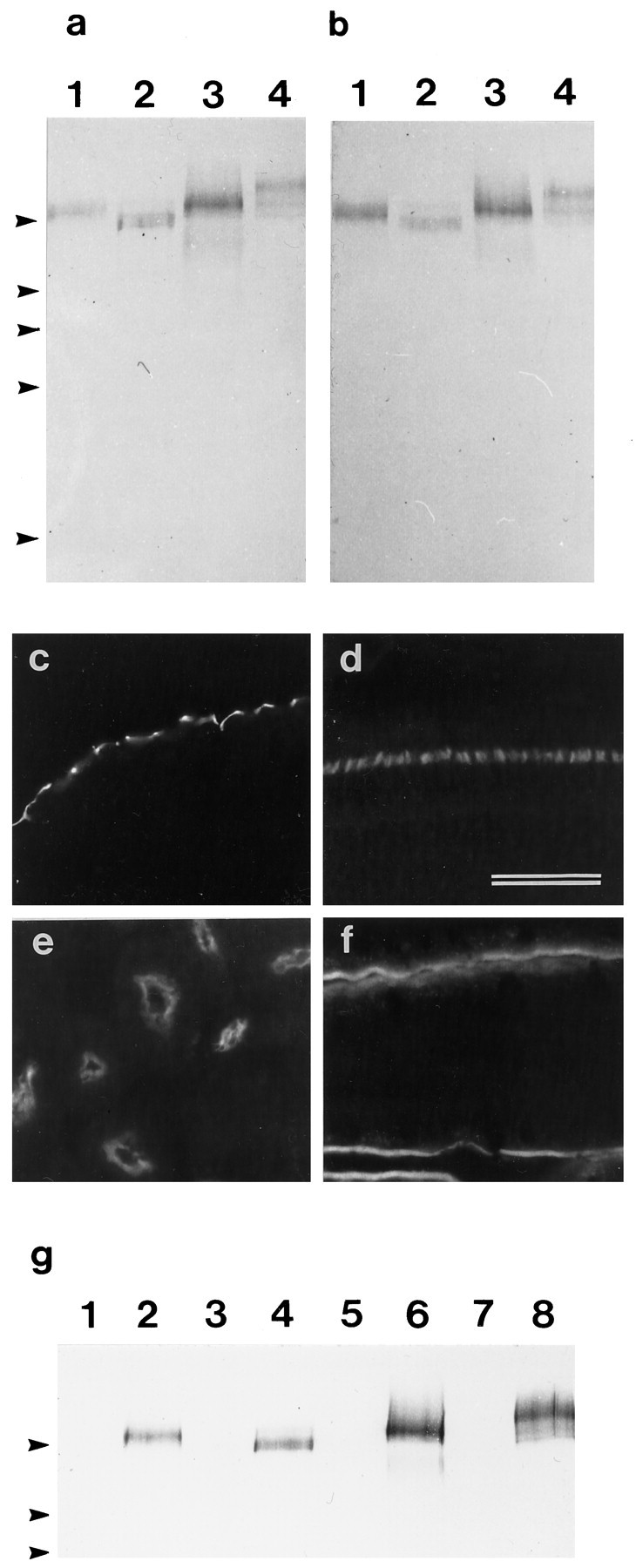
a, b, Immunoblots of Triton X-100-soluble fractions prepared from the lagenar macula (1), retina (2), kidney (3), and intestine (4) that have been stained with mAb D37 (a) and affinity-purified rabbit antibodies raised to a bacterially expressed fusion protein containing part of the extracellular domain of the SCA (b). Arrowheads indicate the positions of markers with molecular masses (from top tobottom) of 205, 116, 96, 66, and 45 kDa.c–f, Immunofluorescence micrographs of cryosections from the basilar papilla (c), retina (d), kidney (e), and small intestine (f) that have been stained with the affinity-purified rabbit antibody directed against the extracellular domain of the SCA. The staining patterns are identical to those observed with the mAb D37 shown in Figure 3. Scale bar, 50 μm.g, Immunoblot stained with mAb D37 of proteins immunoprecipitated from Triton X-100-soluble fractions of lagenar macula (1, 2), retina (3, 4), kidney (4, 5), and small intestine (7, 8) with rabbit preimmune serum (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7) or rabbit immune serum to the extracellular domain of the SCA (lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8).Arrowheads indicate the positions of markers with molecular masses (from top to bottom) of 205, 116, and 96 kDa.
