Fig. 2.
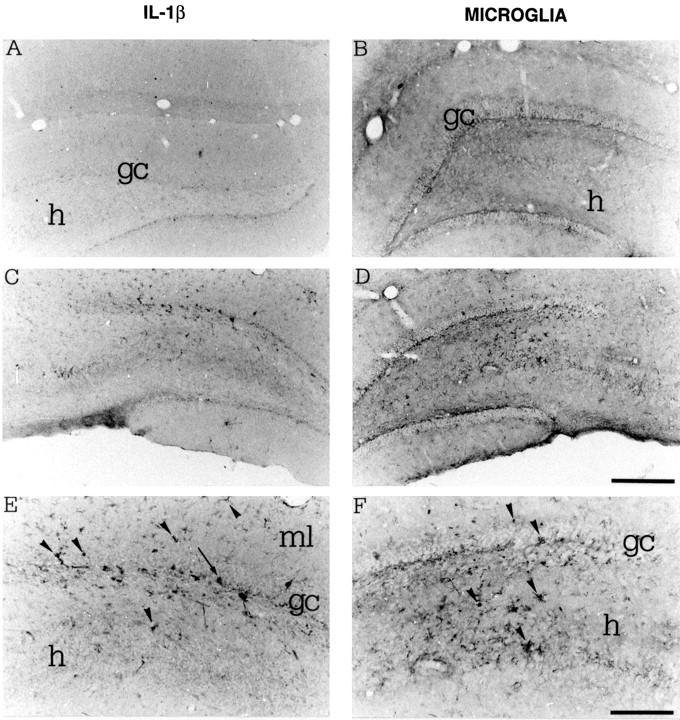
Photomicrographs showing IL-1β immunoreactivity (A, C, E) and B4-isolectin-positive microglia (B, D, F) in coronal sections of the rat dorsal hippocampus 3 hr after a local injection of PBS saline (A, B) or 0.19 nmol of kainic acid (C–F). E, F, Higher magnifications of pictures respectively depicted inC and D. IL-1β immunoreactivity was markedly increased in glia-like cells located in the granule cell layer and in the molecular layer (ml) of the dentate gyrus (arrowheads). These cells have a darkly stained cell body and branched processes, and some of them have an ameboid shape resembling microglia phenotype (E). Scattered cells with neuronal appearance were also observed (E, arrow). B4-isolectin-positive microglia was also increased in the same regions (D, F). Note that microglia cells and their processes were interposed between granule cells (gc) and CA3 pyramidal neurons in the hilus (h). Scale bars: A–D, 500 μm;E, F, 200 μm.
