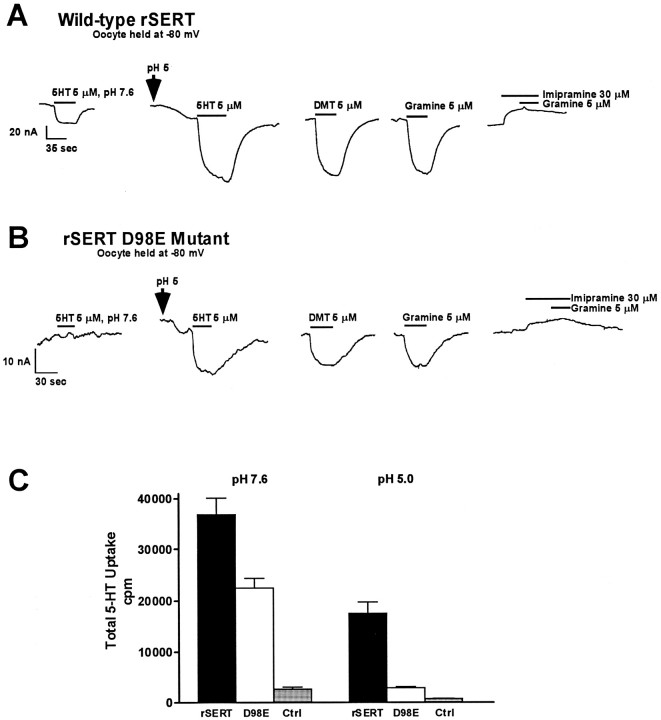
Fig. 4.
rSERT D98E mutant does not demonstrate substrate-induced current at pH 7.6. Xenopus oocytes were injected with either wild-type rSERT (A) or D98E mutant (B) cRNA, and two-electrode voltage-clamp experiments were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Oocytes were held at −80 mV and perfused with various tryptamines as indicated. For wild-type rSERT, the 5HT-activated current observed at pH 7.6 was augmented at pH 5.0. Also, the shift to pH 5.0 induced an inward current in the absence of 5HT, consistent with previously published results (Cao et al., 1997). DMT and gramine experiments were performed at pH 5.0 to increase substrate-induced currents. The transporter antagonist imipramine was capable of inhibiting both 5HT- (data not shown) and gramine-induced currents. For the D98E mutant (B), 5HT-activated current was not detectable above background at pH 7.6. Substrate-induced currents were observed at pH 5.0, although the magnitude of the inward current was greatly reduced (note change in scale between A andB). No substrate-induced currents at either pH 7.6 or 5.0 were observed for water-injected or uninjected oocytes (data not shown). The results shown are from single oocytes expressing either wild-type rSERT or the D98E mutant and are representative of data from six separate oocytes. C, Comparison of [3H]5HT uptake in Xenopus oocytes injected with wild-type rSERT or D98E cRNA. Oocytes injected with wild-type rSERT cRNA, D98E mutant cRNA, or water (control) were incubated in the presence of 10 nm[3H]5HT for 30 min in room temperature Ca2+-Ringer’s, pH 7.6 or 5.0, as described in Materials and Methods. Data represent total [3H]5HT uptake (cpm) (n = 9).