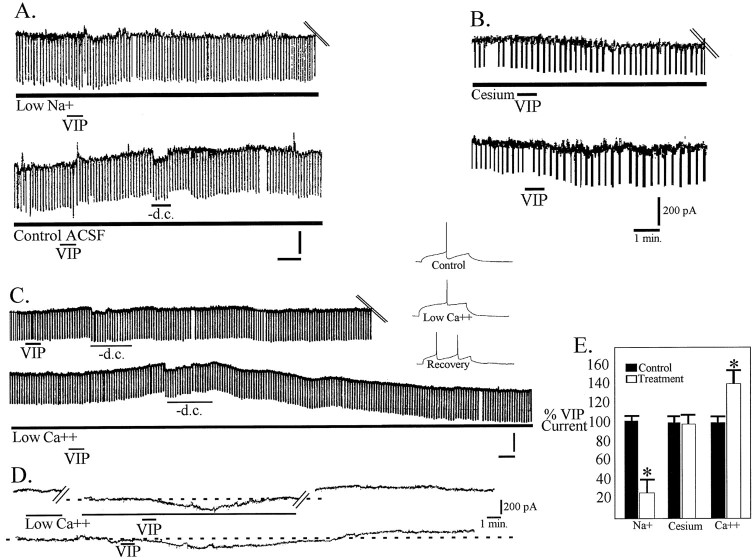
Fig. 4.
VIP induces a sodium-dependent depolarization.A, Bridge mode recordings of the response of a cell to 100 nm VIP in the presence of choline-substituted low-sodium ACSF. After washout of the low-sodium solution, VIP application was repeated in the presence of control ACSF. Calibration: 5 mV, 1 min. B, VIP (100 nm) applied for 30 sec in the presence of 1 mm cesium (top trace) induced an inward current that was not significantly different from in control conditions (bottom trace).C, Bridge mode recordings of the response to 100 nm VIP applied for 30 sec in normal ACSF (top trace) and after washout in 0.5 mmCa2+–10 mm Mg2+solution. High-gain records (inset) demonstrating loss of AHP after 20 min exposure to low-Ca2+ solution.D, Voltage-clamp recordings of the inward current induced by VIP in low-Ca2+ solution (top trace) and after washout in normal ACSF (bottom trace). E, Bar graph quantifying the results of ion substitution experiments.