Fig. 16.
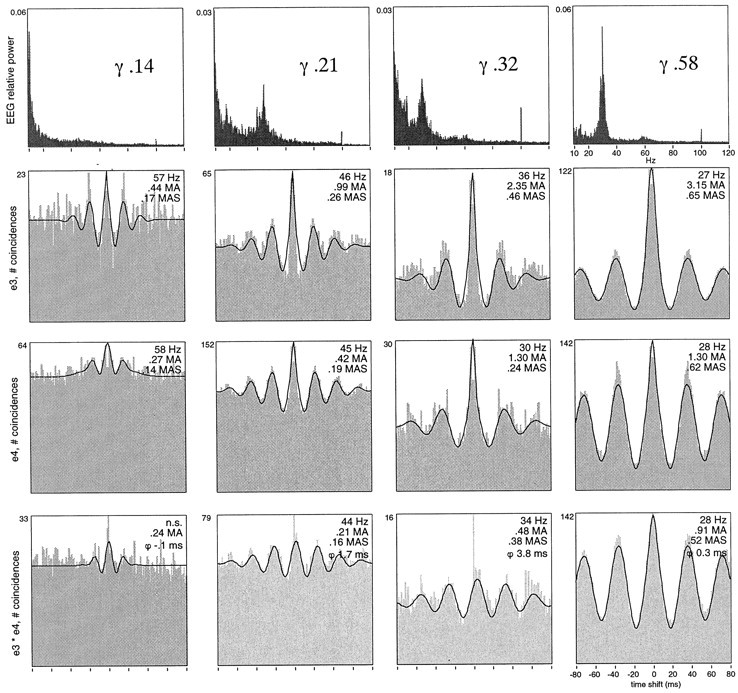
Covariation of EEG γ activity with oscillation frequency, oscillatory modulation, local synchronization, and intrahemispheric synchronization of visual responses recorded from two sites in A17 (e3, e4, same as in Fig.15). Top row, Averaged EEG power spectra at four nonconsecutive time points, the second one having been obtained during MRF stimulation. Numbers refer to relative γ power in the respective epochs. Second row, Averaged auto-correlation functions of visual responses recorded during corresponding epochs from site e3; third row, averaged auto-correlation functions of responses from e4; bottom row, averaged cross-correlation functions of visual responses across sites e3 and e4. For each correlogram, oscillation frequency (hertz), oscillation strength (MAS), and synchronization strength (MA) and phase (ϕ, milliseconds) are indicated. With increasing relative γ content in the EEG (left to right columns), the oscillation frequency of the visual responses decreases from ∼60 to <30 Hz at both sites. At the same time, the strength of oscillatory modulation of local synchronization and of synchronization across the sites increases.
