Fig. 9.
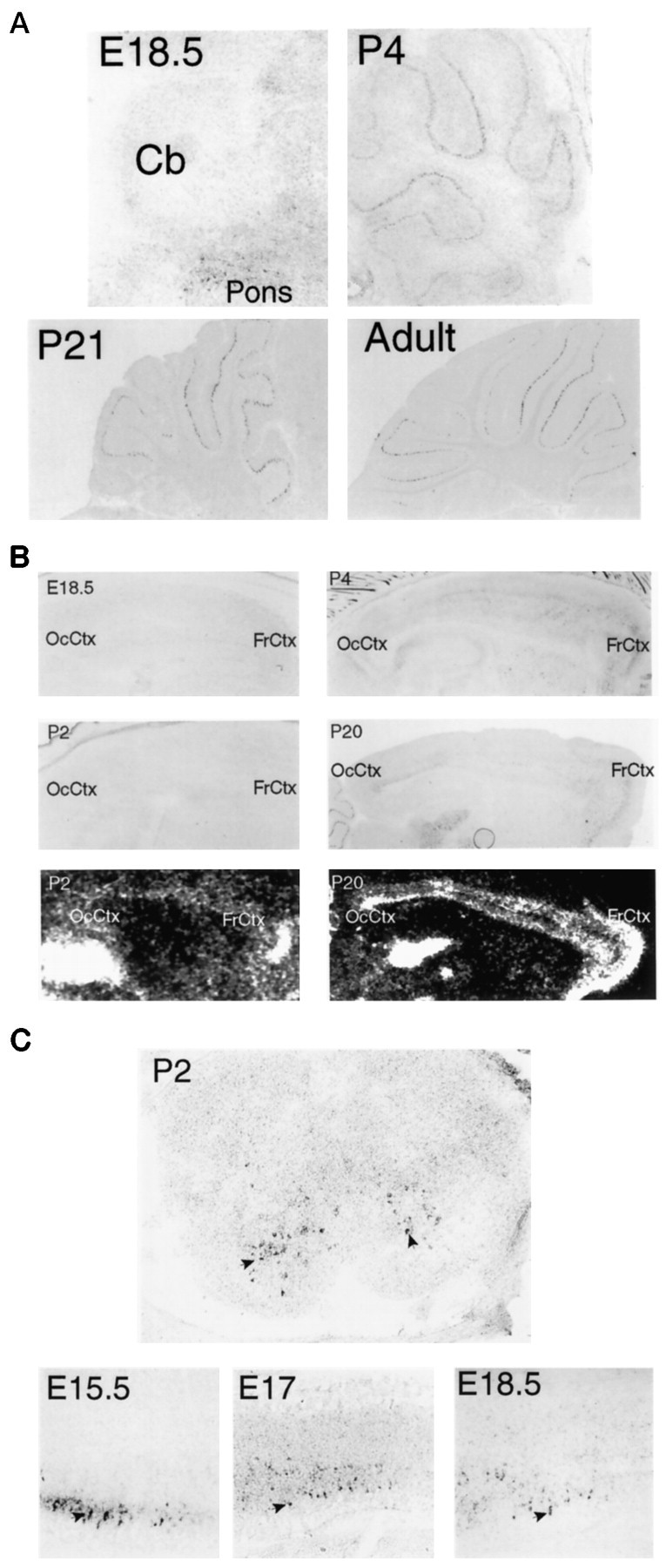
A, Developmental expression of encephalopsin in the cerebellum is shown. The adult pattern of encephalopsin expression is not seen until several weeks after birth. Sagittal sections are shown. E18.5 is taken at 100×, P4 is taken at 50×, and P21 and adult are taken at 25×. B, Developmental expression of encephalopsin expression in the cerebral cortex is shown. Encephalopsin expression is absent prenatally, relatively evenly distributed throughout the cortex in the early postnatal mouse, and showing rostrocaudal gradients and regional organization by P20. Digoxy genin in situ hybridization is shown for E18.5, P2, P4, and P20, whereas radioactive in situhybridization (bottom) is shown for P2 and P20. Digoxygenin in situ hybridization pictures are taken at 50× for E18.5, 25× for P2 and P4, and 12.5× for P20.C, Encephalopsin expression is prominent in developing spinal cord. Sagittal sections of embryonic time points are taken of the cervical cord at 100× for E15.5 and 50× for E17 and E18.5. The coronal section at P2 is taken of cervical spinal cord at 50×.Arrows indicate selected encephalopsin-positive interneurons of the ventral horn. The color reaction in the P2 section is allowed to proceed twice as long as that in the embryonic time points, so the observed abundance levels of encephalopsin are not directly comparable. Cb, Cerebellum;FrCtx, frontal cortex; OcCtx, occipital cortex.
