Fig. 2.
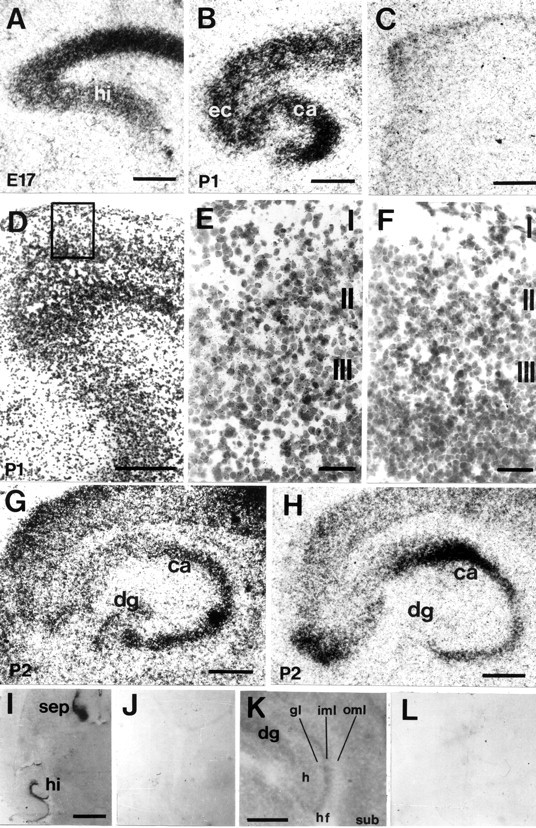
Distribution of EphA5 (A–F), ephrin-A3 (G), ephrin-A5 (H) mRNA and EphA5-AP fusion protein binding (I–L) in the developing entorhino-hippocampal system on horizontal sections. A, At E17, strong hybridization signals for EphA5 mRNA signals were found in the cortex and hippocampal primordium. B, At P1, EphA5 expression was localized in the cortex, EC, and subiculum. In the hippocampus, strong hybridization signals were present in the pyramidal cell layers of CA1–CA3. C, Sense control for EphA5in situ hybridization showed no specific labeling.D, Emulsion-coated EphA5 in situhybridization of the entorhinal cortex; the boxed areais shown in higher magnification in E. E, At P1, EphA5 expression was localized to layers II and III of the EC, whereas no specific labeling could be observed with the sense control (F). G, At P2, ephrin-A3 mRNA was expressed in the cortex, the CA1–CA3 regions, and the granular cell layer of the dentate gyrus. H, Ephrin-A5 mRNA was localized in the CA pyramidal cell layers from P2 onward but not in the dentate gyrus. I, EphA5-AP fusion protein binding could be localized in the hippocampus and the septum, whereas negative control using alkaline phosphatase detection alone did not show binding signals (J). K, In the hippocampus, EphA5-AP fusion protein binding was strongest in the inner molecular layer of the dentate gyrus and low in the outer molecular layer; no specific labeling could be observed with the negative control (L). hi, Hippocampus;sep, septum; CA, Cornu ammonis;dg, dentate gyrus; ec, entorhinal cortex;gl, granular layer; oml, outer molecular layer; iml, inner molecular layer; hf, hippocampal fissure; sub, subiculum. Scale bars:A–C, G, H,K, 500 μm; D, I, 1 mm;E, F, 100 μm.
