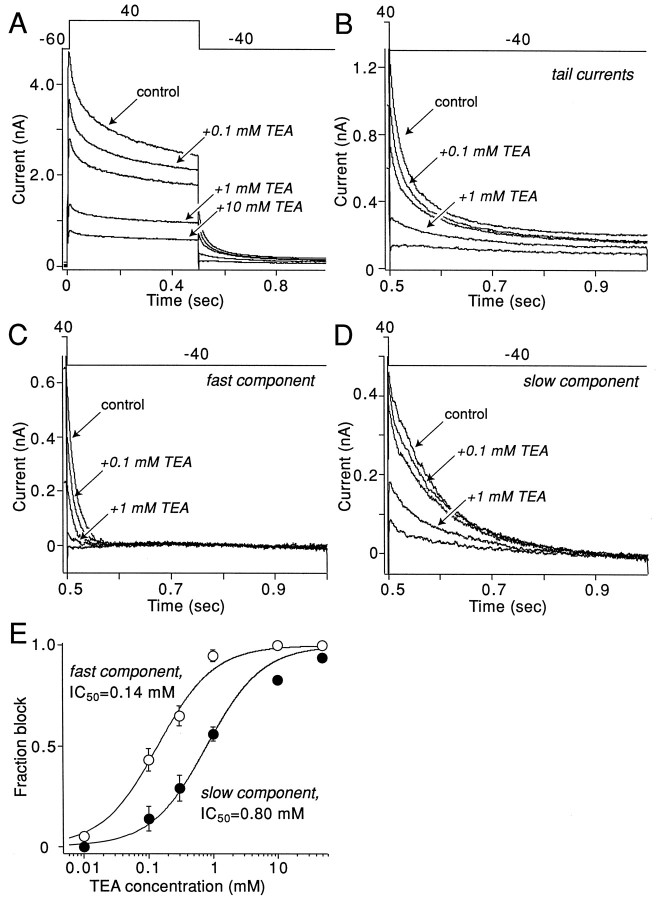
Fig. 2.
TEA differentially blocks rapidly and slowly deactivating currents. A, Currents evoked in the presence of different concentrations of TEA by the voltage-clamp protocol shown above the traces. B, Tail currents at −40 mV obtained during the experiment shown inA. C, Rapidly deactivating tail currents in increasing concentrations of TEA obtained by the subtraction method described in Figure 1. D, Slowly deactivating tail currents in increasing concentrations of TEA. E, Plot of rapidly and slowly deactivating tail current amplitudes as a function of TEA concentration. The lines represent Langmuir first-order fits of experimental data.