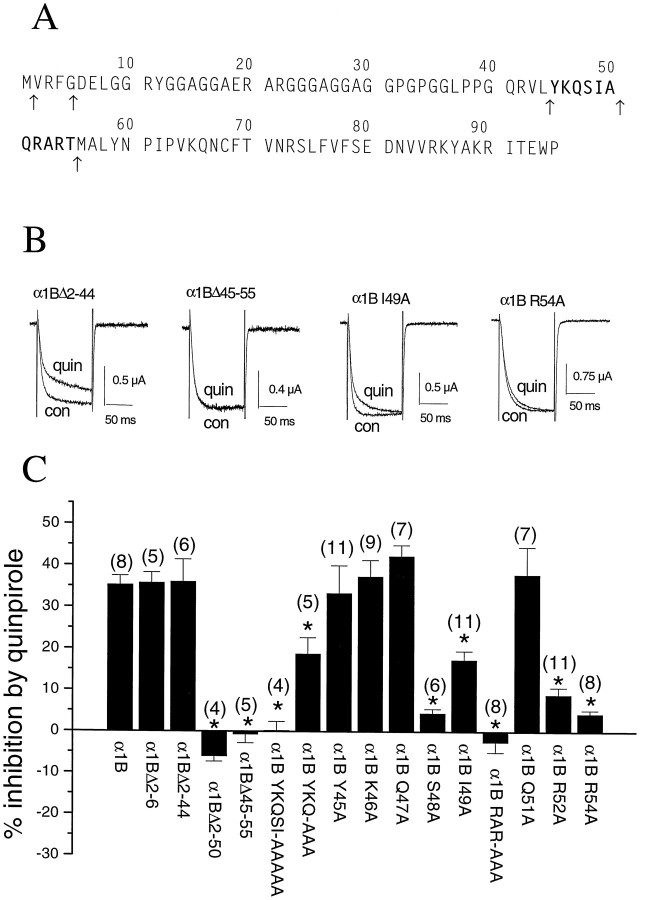
Fig. 5.
The effect of various deletions and point mutations of the N terminus of α1B on inhibition ofIBa by the D2 agonist quinpirole. The sequence of the N terminus of α1B, with the 11 amino acid sequence identified as being involved in G-protein modulation inbold, and the points at which deletions were made shown by arrows beneath the sequence. Example traces, showing the effect of quinpirole (100 nm) onIBa in the α1B Δ2–44 mutant (left), the α1B Δ45–55 mutant (center left), the α1B I49A mutant (center right), and the α1B R54A mutant (right). Traces (100 msec duration) were obtained at a test potential of 0 mV, from a holding potential of −100 mV. Con, Control traces;quin, after perfusion of quinpirole. Histogram of the percentage inhibition by 100 nm quinpirole (mean ± SEM) of IBa in the various deletion and point mutants of the N terminus of α1B. The currents were activated at 0 mV, and the degree of inhibition was determined from the currents activated every 15 sec. The number of experiments for each condition is given in parentheses, and the significance of the differences compared to the inhibition of α1B are given by *p < 0.005.