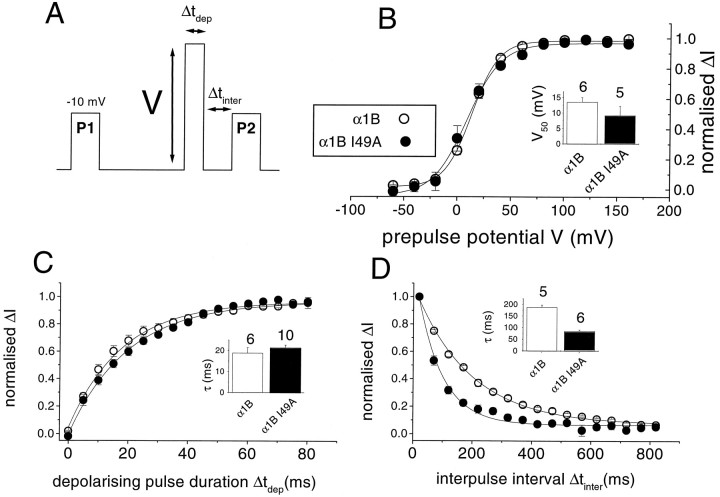
Fig. 8.
Voltage dependence of inhibition, rate of loss of inhibition, and reinhibition rate for α1B and α1B I49A inXenopus oocytes. A, Voltage protocol, showing variation of the prepulse voltage (V), the prepulse duration (Δtdep), and the interpulse interval (Δtinter) between the prepulse and the test pulse. The prepulse potential was 100 mV and 50 msec duration, and the interpulse interval was 20 msec, unless these parameters were varied.B, Effect of increasing the 50 msec prepulse voltage (V) on prepulse facilitation in the presence of quinpirole. Facilitation was measured as (IBa in P2) − (IBa in P1) and normalized to the maximum facilitation observed (normalized ΔI). α1B (open circles), α1B I49A (filled circles). The inset histogram gives theV50 values (mean ± SEM, determined by fitting Boltzmann functions to the data from the number of individual experiments given above each bar) for α1B (white bar) and α1B I49A (black bar). C, Effect of increasing the duration of the 100 mV prepulse (Δtdep) on prepulse facilitation in the presence of quinpirole. Facilitation was measured as described inB. α1B (open circles), α1B I49A (filled circles). The insethistogram gives the τdissociation values (mean ± SEM, determined by fitting a single exponential to the data from the number of experiments given above each bar) for α1B (white bar) and α1B I49A (black bar).D, Effect of increasing the interval between the 100 mV, 50 msec prepulse and the subsequent test pulse P2 on the facilitation in the presence of quinpirole. Facilitation was measured as described in B: α1B (open circles), α1B I49A (filled circles). The insethistogram gives the τreinhibition values (mean ± SEM, determined by fitting a single exponential to the data from the number of experiments given above each bar) for α1B (white bar) and α1B I49A (black bar).