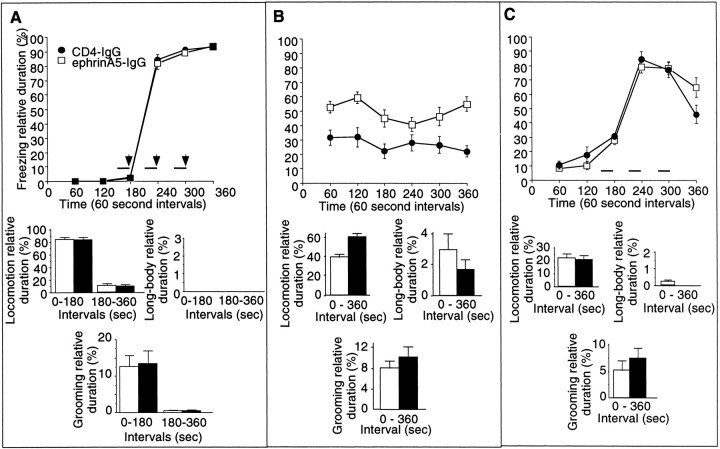
Fig. 7.
EphrinA5-IgG infusion significantly improves learning performance in a context-specific manner in fear conditioning in DBA/2 strain of mice. Methods are described in detail previously (Gerlai, 1998b). A, In the training session, no significant differences were found between ephrinA5-IgG-infused (white squares; n = 19 for training and tests) and CD4-IgG-infused (black circles;n = 17 for training and tests) mice in any of the behaviors (freezing: line diagram; other behavioral elements: bar graphs) measured, suggesting normal perceptual and motor performance.B, Response to contextual stimuli is shown. The freezing performance (line diagram) of ephrinA5-IgG-infused mice was significantly improved compared with the CD4-IgG-infused animals throughout the test session (F(1,34) = 33.434; p < 0.0001). In addition to freezing, increased level of fear in EphrinA5-IgG-infused mice is also indicated by changes in other behavioral elements (bar graphs). C, In the cued test, mice were placed in a chamber in which contextual stimuli were different from those of the shock chamber as explained in Figure 5C. The mice received three tone signals alone (solid horizontal bars) but no shock. All mice responded to the tone cue with a robust increase in freezing (line diagram), and no significant difference was found between the two groups of mice in freezing (F(1,34) = 0.004;p > 0.95) or in any of the other behavioral measures (bar graphs) analyzed.