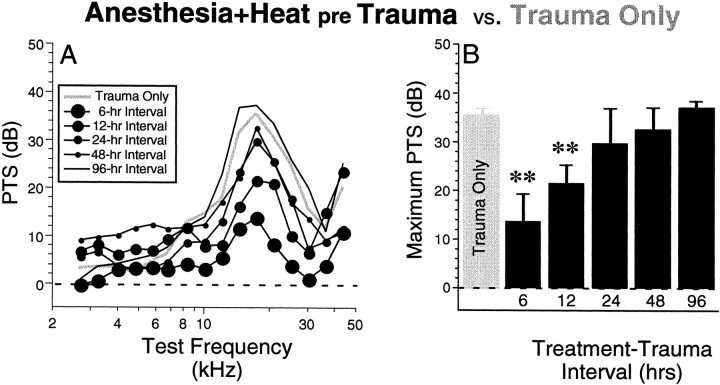
Fig. 4.
Heat stress significantly reduces PTS from a subsequent acoustic overexposure. A compares mean PTS for five Anesthesia+Heat pre Trauma groups with theTrauma Only group. All thresholds are normalized to the mean control thresholds seen in nontraumatized mice (Fig. 3).B examines the effect of treatment–trauma interval by replotting the maximum PTS (i.e., the value at 17.5 kHz) from each graph in A, arranged with increasing time interval between heat stress and trauma. SE bars are shown; **p < 0.005 indicates significant group difference between a given experimental group and the Trauma Onlygroup (ANOVA). Tests were performed as a series of two-way ANOVAs (factors are frequency and group), each of which compared all PTS values obtained at test frequencies between 7 and 40 kHz from a particular experimental group with comparable data from the control group.