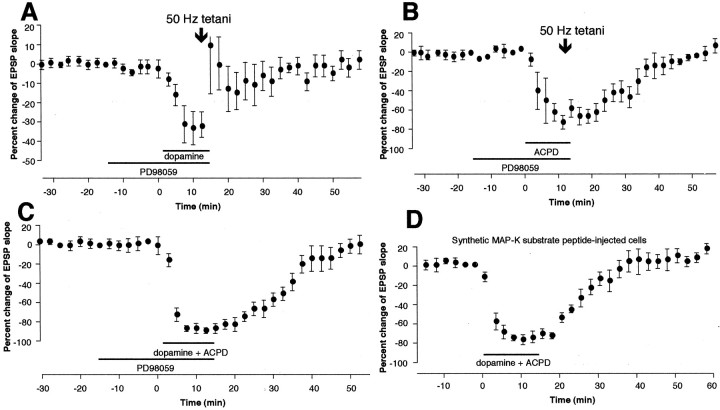
Fig. 10.
LTD induction in prefrontal cortex requires activation of MAP-Ks. A, LTD by 50 Hz tetani in the presence of dopamine (Fig. 1E) was blocked by bath application of PD98059 (20 μm), the specific inhibitor of MAP-K kinases (MEK1 and MEK2, which phosphorylate ERK1 and ERK2). Mean change of the EPSP slope measured 35–40 min after drug washout–tetani was 0.3 ± 4.1% (n = 6,p < 0.02 vs dopamine + tetani group depicted in Fig. 1E). B, LTD by 50 Hz tetani in the presence of 1S,3R-ACPD (Fig.6A) was also blocked by bath application of PD98059. Mean change of the EPSP slope measured 35–40 min after drug washout–tetani was −0.6 ± 3.9% [n = 4,p < 0.002 vs 1S,3R-ACPD + tetani group (Fig.6A)]. C, LTD by coactivation of dopamine receptors and groups I and II mGluRs with 1S,3R-ACPD (Fig. 9A) is blocked by PD98059. Mean change of the EPSP slope measured 35–40 min after drug washout was −4.9 ± 5.8% (n = 6,p < 0.02 vs the group depicted in Fig.9A). D, LTD by dopamine + 1S,3R-ACPD coapplication is also blocked by postsynaptic injection of specific synthetic MAP-K substrate peptide Ala-Pro-Arg-Thr-Pro-Gly-Gly-Arg-Arg (1 mm in electrode). This peptide, when abundantly present, acts as a specific competitive inhibitor against endogenous MAP-K substrates. Mean change of the EPSP slope 35–40 min after drug washout was 8.4 ± 6.2% [n = 5, p < 0.001 vs dopamine + 1S,3R-ACPD group (Fig.9A)]. Thus, critical MAP-K activation for LTD induction after coactivation of dopamine receptors and mGluRs occurs in postsynaptic sites.