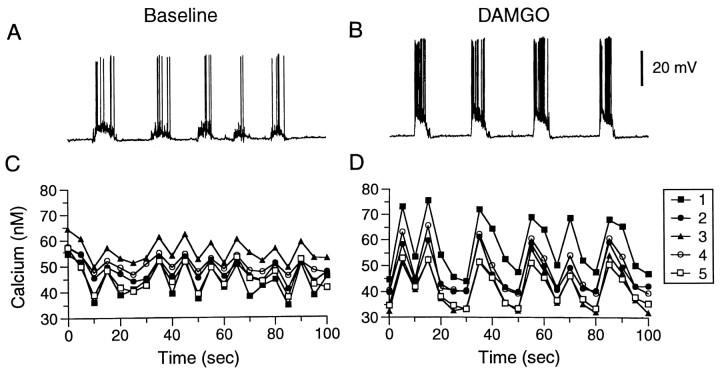
Fig. 5.
DAMGO alters spontaneous, synaptically driven burst activity in hippocampal neurons. A,B, Electrophysiological recordings of spontaneous burst activity in a cultured pyramidal-like hippocampal neuron under baseline control conditions and after the addition of DAMGO (1 μm) to the bath saline. The neuron exhibited repetitive burst activity under control conditions. The amplitude of the membrane depolarization during the burst and the number of spikes that were evoked were enhanced in the presence of DAMGO. C, D, For comparison purposes, representative recordings of intracellular Ca2+ oscillations are shown under the same conditions as in electrophysiological studies. The Ca2+ recordings are from in five neurons in a microscopic field. The time scale is the same for the intracellular Ca2+ and electrophysiological recordings. Note the similarity in the pattern of activity of spike bursts and intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in the presence of DAMGO.