Fig. 4.
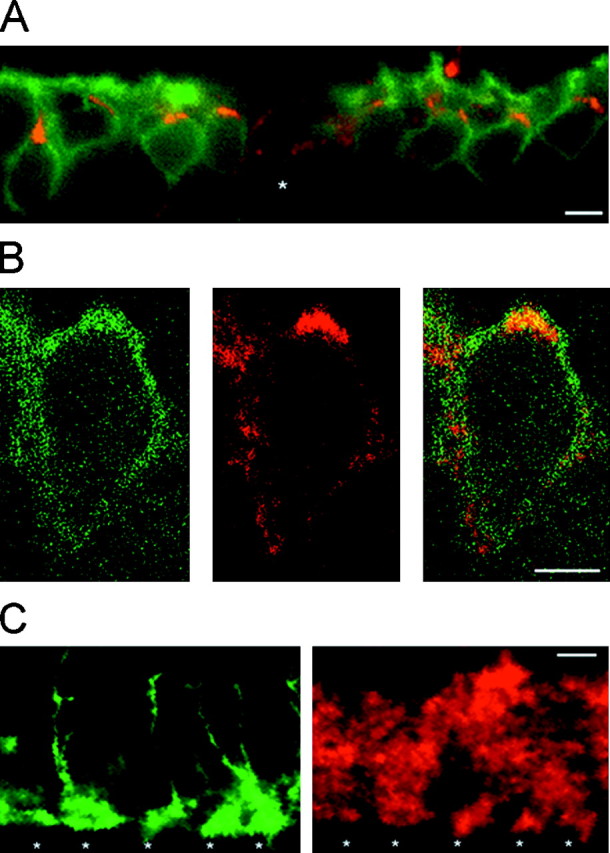
Subcellular distribution of ClC-2 on rod bipolar cells. A, Enlarged view of a vertical cryostat section immunolabeled as in Figure 3. Cell bodies of rod bipolar cells were located in the outer half of the inner nuclear layer (green fluorescence). ClC-2 immunoreactivity (red fluorescence) was present on every cell body, resulting in yellow signals. In addition, ClC-2 staining outlined other cells (star). B, Horizontal single-section confocal fluorescence micrographs of a rod bipolar cell body double-immunolabeled as described in Figure 3. PKC immunoreactivity was predominantly localized to the cell membrane (left, green fluorescence). Expression of ClC-2 is shown in the middle (red fluorescence). The double exposure demonstrated that ClC-2 immunoreactivity seemed to be mostly present within or near the cell membrane (right, yellow).C, Enlarged view of the lower border of the IPL of double-labeled vertical cryostat sections. Axon terminal systems of rod bipolar cells were double-immunolabeled with antibodies recognizing PKC (left, green fluorescence). ClC-2 immunoreactivity (red fluorescence) was present at identical positions (stars). Furthermore, ClC-2 immunoreactivity was observed at other regions within the IPL. Scale bars: A, C, 10 μm; B, 5 μm.
