Fig. 6.
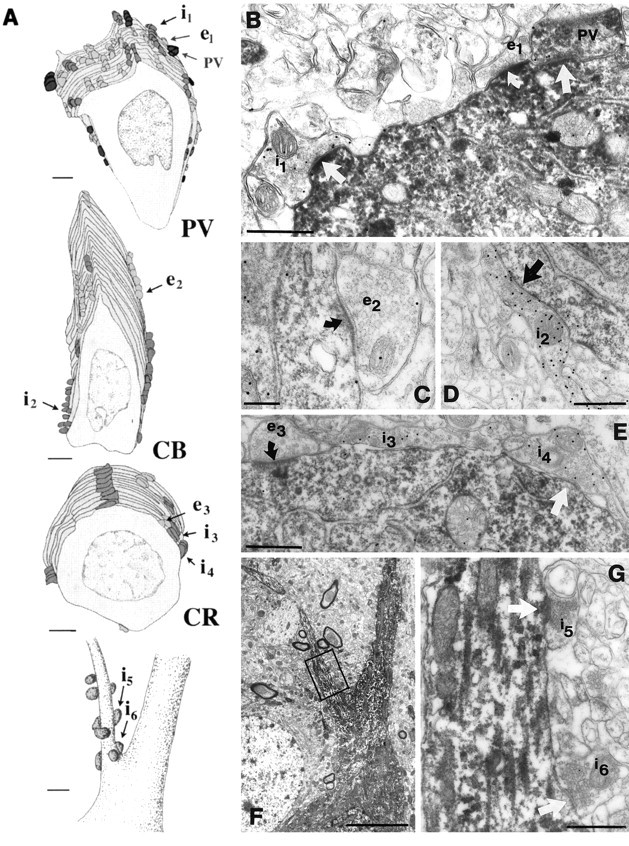
Afferents on the somata and axon initial segments of interneurons. A, Partial reconstructions of the somatic inputs of a PV, a CB, and a CR neuron, as well as the distribution of axo-axonic synapses on the axon initial segment of a PV neuron. Inhibitory cells receive both excitatory (light gray) and inhibitory (dark gray andblack) inputs onto their somata. A large proportion of the somatic inhibitory terminals on the PV somata came from PV-positive axon terminals (black). Eight to twelve axo-axonic synapses terminate on the axon initial segment of an interneuron. Innervation of the axon initial segment of a PV neuron is shown at thebottom of the panel. The axo-axonic synapses clustered close to the soma at the very beginning of the axon initial segment. Terminals labeled i1–i6 and e1–e3 are shown in electron micrographs in B–G. B,The three types of somatic input arriving onto PV cells are shown in the electron micrograph. Bouton e1 is a GABA-negative (presumed excitatory) terminal. Similar to the dendritic contacts, GABA-positive terminals could be PV-positive (PV) or negative (i1). C–E, CB- and CR-positive somata also received GABA-negative (excitatory, e2, e3) and GABA-positive (inhibitory, i2, i3-i4) synapses, but in a lower density than PV-containing somata. F, G, Low- and high-power electron micrographs of the axon initial segment (A) receiving symmetrical synapses. Note inA that the proportion of inhibitory terminals is higher in the somatic region than in the dendritic tree for all examined populations. In B–E and G,curved arrows indicate asymmetrical synapses, arrowsindicate symmetrical synapses. Scale bars: A, 2 μm for somata, 1 μm for AIS; B, D,E, G, 0.5 μm; C, 0.25 μm; F, 5 μm.
