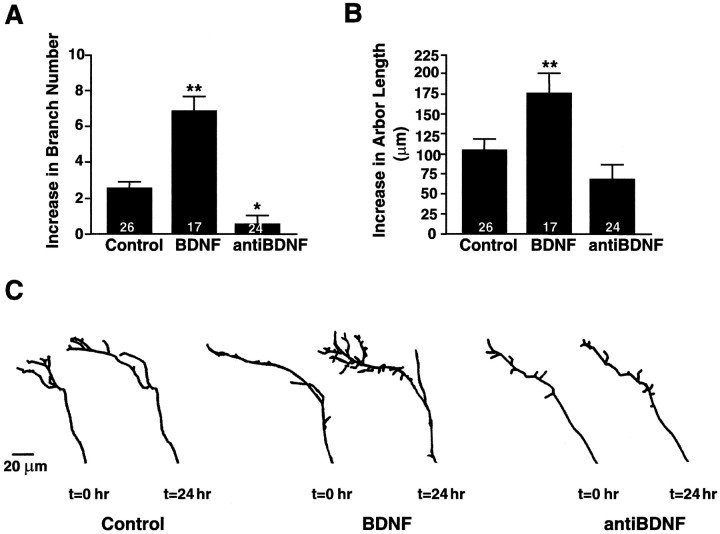
Fig. 7.
BDNF enhances RGC axonal arborization in vivo. Time-lapse analysis of DiI-labeled RGC axon arbors reveals that the morphology of RGC axonal arbors is influenced by tectal BDNF levels (also see Cohen-Cory and Fraser, 1995). A, B, The effects of BDNF and anti-BDNF on RGC axon arbor morphology after 24 hr of treatment were evaluated by measuring quantitatively the total branch number (A) and total arbor length (B). Values are presented as the change from their initial value at the time of treatment. The significant increase in total branch number and arbor length elicited by BDNF reflects an overall increase in axon arbor complexity versus controls. Similarly, the significantly lower increase in branch number elicited by anti-BDNF indicates that neutralizing endogenous BDNF prevents the increase in axon terminal arbor complexity that normally occurs over time in normal tadpoles. Values represent the averages; error bars indicate ± SEM. **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 as compared with control.C, Tracings of representative axonal arbors before and 24 hr after control, BDNF, or anti-BDNF injections illustrate the effects of each treatment on RGC axon arbor complexity. Controls include axons from tadpoles treated with vehicle solutions or with nonimmune IgGs. Scale bar, 20 μm.