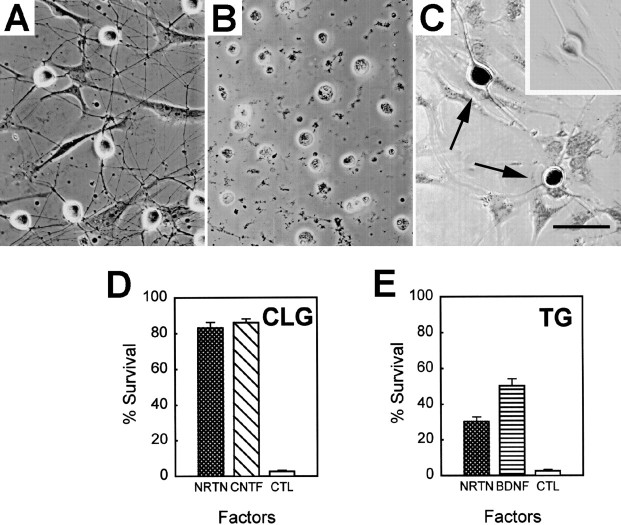
Fig. 5.
Effects of NRTN on the survival of E9 ciliary and trigeminal ganglion neurons. A, Dissociated E9 ciliary ganglion neurons grown in the presence of 50 ng/ml NRTN.B, Dissociated E9 ciliary ganglion neurons grown in the absence of trophic factors. C, Dissociated E9 trigeminal ganglion neurons grown for 2 d in the presence of 50 ng/ml NRTN and subsequently stained for Ret. All cells with neuronal morphology are positive with Ret staining (arrows), whereas flat non-neuronal cells are devoid of staining. A neuron probed with the primary antibody that was preincubated with a blocking peptide shows no staining (inset). Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Survival of E9 ciliary ganglion neurons in the presence of 50 ng/ml NRTN or CNTF in comparison with control (no factor). E, Survival of E9 trigeminal ganglion neurons in the presence of 50 ng/ml NRTN or BDNF in comparison with control. Results are expressed as the percentage of the neurons that survived after 48 hr in culture (± SE). Note that the majority of E9 ciliary ganglion neurons is supported by NRTN (D), whereas only a subpopulation of E9 trigeminal ganglion neurons is NRTN-dependent (E).