Fig. 12.
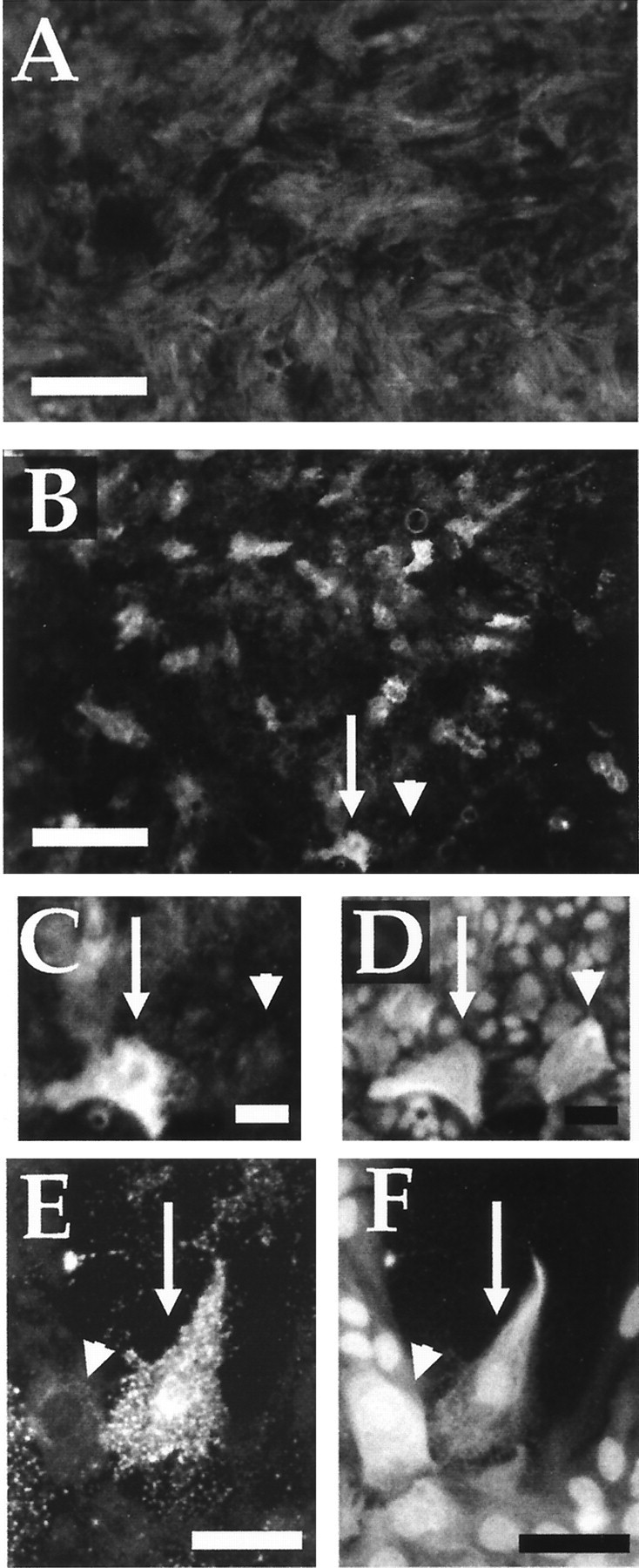
Inflammation in vitro leads to heterogeneous increases in proteoglycans in astrocyte cultures. Areas of the in vitro cavitation model were stained for chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (A–C, E) or GFAP (D, F). A, Astrocytes with nonactivated macrophages demonstrate a uniform low level of proteoglycan staining in control cultures, a result that is also seen in astrocyte cultures with zymosan only or with nonactivated macrophage–conditioned media (data not shown). B–D, In contrast, individual cells with increased levels of proteoglycans can be observed in astrocyte cultures containing activated macrophages (data not shown) or in astrocyte-only cultures with activated macrophage–conditioned media (B). Thearrow and arrowhead in Bindicate two astrocytes shown in high power in C(proteoglycan) and D (GFAP). One astrocyte has increased proteoglycan staining (arrow), whereas the other nearby astrocyte has no such increase (arrowhead). E, F, High-power view is shown of two astrocytes (arrow and arrowhead) in which one has increased proteoglycan staining (E) whereas the other does not in an astrocyte culture (GFAP inF) with activated macrophages. Scale bars:A, B, 210 μm; C, D, 40 μm; E, F, 60 μm.
