Fig. 9.
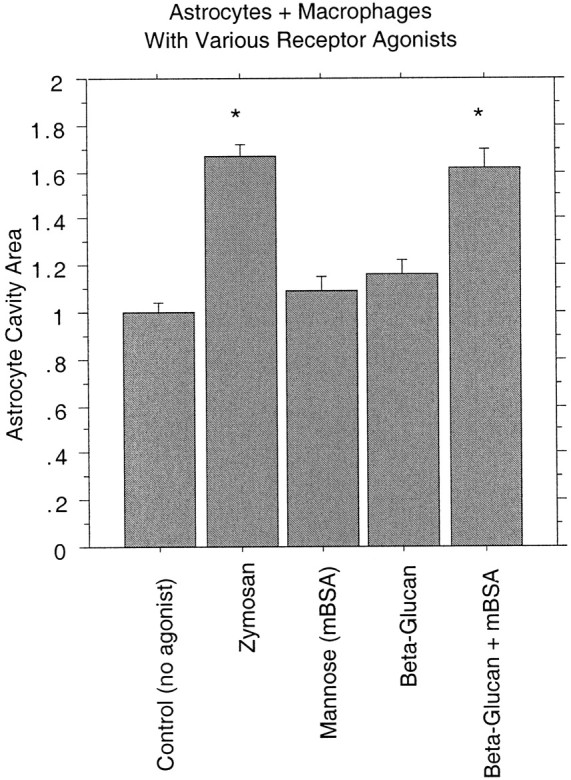
Simultaneous activation of both the macrophage mannose receptor and the β-glucan–binding site of CR3 on macrophages induces astrocyte cavitation in the in vitro astrocyte cystic cavitation model. Each receptor agonist category is expressed relative to simultaneous control (no agonist) nonactivated macrophage and astrocyte cocultures set to a value of 1, and all replicates are combined for each category. Astrocyte monolayers were established, and peritoneal macrophages were added with no activating stimulant [Control(no agonist); nonactivated macrophages] or with various receptor agonists (zymosan, mBSA, β-glucan, or β-glucan + mBSA). Mannose receptor agonists alone (mBSA) or CR3 β-glucan site agonists alone (purified particulate β-glucan) were not sufficient to activate the macrophages to induce the formation of astrocyte cavities in vitro. However, addition of both mBSA and β-glucan simultaneously as macrophage activators in the macrophage and astrocyte coculture mimicked the development of astrocyte cavities induced by the zymosan stimulation of macrophages. ANOVA with reported significance is relative to the control (no agonist) nonactivated macrophage preparation or conditioned media, and the graph reports group means ± SEM (*p < 0.0001).
