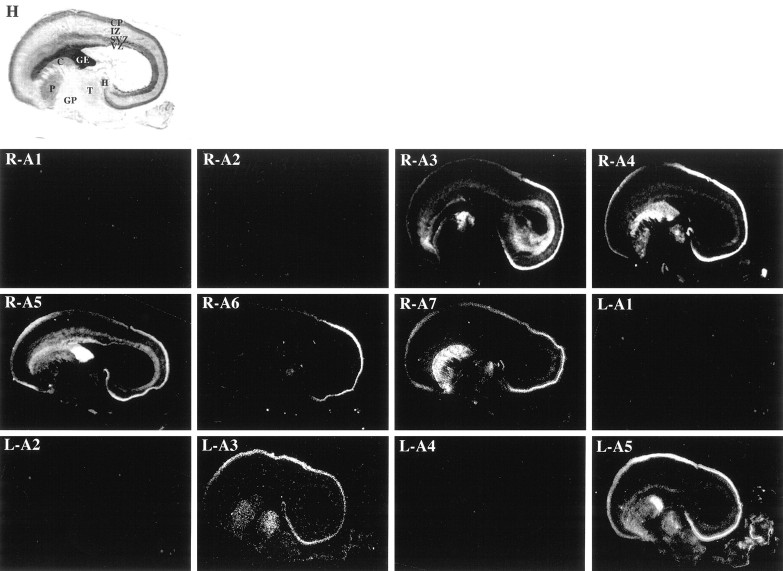
Fig. 3.
Expression of the EphA receptors and ephrin-A ligands in the E80 macaque monkey brain. Low-power (1×) views of adjacent parasagittal sections of E80 rhesus monkey brains stained with hematoxylin (H) or processed for radioactive in situ hybridization. Sections hybridized with antisense probes corresponding to EphA1 (R-A1), EphA2 (R-A2), EphA3 (R-A3), EphA4 (R-A4), EphA5 (R-A5), EphA6 (R-A6), EphA7 (R-A7), ephrin-A1 (L-A1), ephrin-A2 (L-A2), ephrin-A3 (L-A3), ephrin-A4 (L-A4), and ephrin-A5 (L-A5) are shown. Embryonic neocortical zones [ventricular zone (VZ), subventricular zone (SVZ), intermediate zone (IZ), and cortical plate (CP)], as well as non-neocortical regions [ganglionic eminence (GE), caudate (C), putamen (P), globus pallidus (GP), thalamus (T), and hippocampus (H)], are labeled in H, and these labels correspond to all sections. Anatomical coordinates for this figure are as in Figure 1.