Fig. 2.
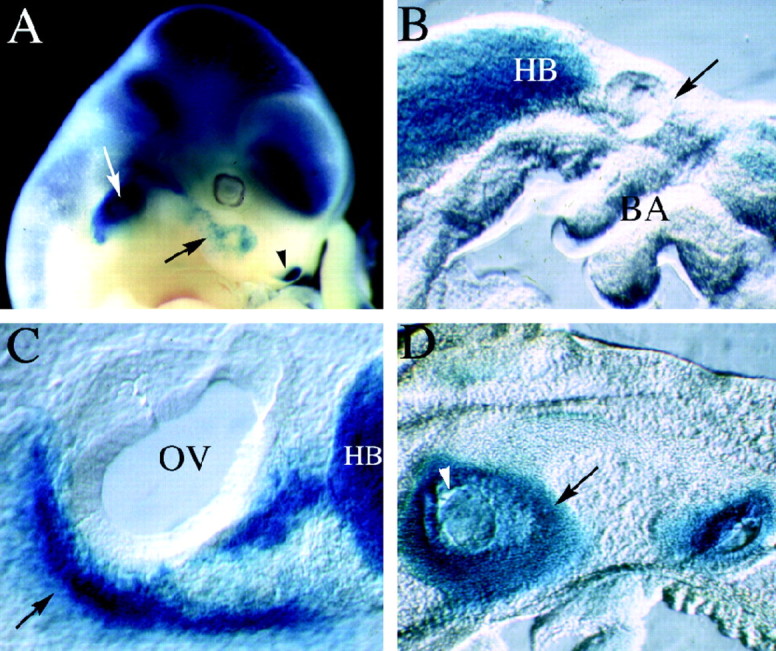
LacZ expression in mutant animals. Mutant embryos were stained with X-gal to visualize the expression of the lacZ gene, which was inserted into the Brn4 locus during the generation of the knock-out allele. Unless specified otherwise the embryos are oriented with rostral to the right and dorsal toward the top. A, The whole-mount preparation of a chimeric founder animal that corresponds to an 11.5 dpc embryo (chimeric embryos are developmentally delayed for ∼1 day because of experimental manipulation of the blastocysts). The expression of lacZ recapitulates precisely the pattern of endogenousBrn4 gene expression detected by hybridization histochemical analyses (Le Moine and Young, 1992; Mathis et al., 1992;Alvarez-Bolado et al., 1995; Phippard et al., 1998). Expression is found throughout most of the neuraxis and in a handful of mesodermally derived tissues in the head, including the otic capsule (white arrow), a small population of first branchial arch mesenchyme (black arrow), and the lateral nasal recess (black arrowhead). B, A parasagittal vibratome section (150 μm) through the otic vesicle of a 9.5 dpc embryo. Expression of lacZ is not detected in the mesenchyme surrounding the otic vesicle (black arrow), which lies dorsal to the branchial arches. However, expression is detected in the hindbrain of these embryos. C, A parasagittal vibratome section through the otic vesicle of a 10.5 dpc embryo. Expression of lacZ is detected in the condensing mesenchyme of the otic vesicle (black arrow), which lies ventral to the otic vesicle at this stage of embryogenesis. In this panel, the black arrow indicates the dorsal–ventral axis, with dorsal corresponding to the upper right-hand corner of the panel.D, Expression patterns of lacZ in a parasagittal section of a 14.5 dpc embryo. At this stage of development, lacZ expression is detected throughout the otic capsule but not in the otic epithelium (some regions of the otic epithelium appear blue, because they are covered with lacZ staining the otic capsule in these thick vibratome sections). BA, Branchial arches;HB, hindbrain; OV, otic vesicle.
