Figure 2.
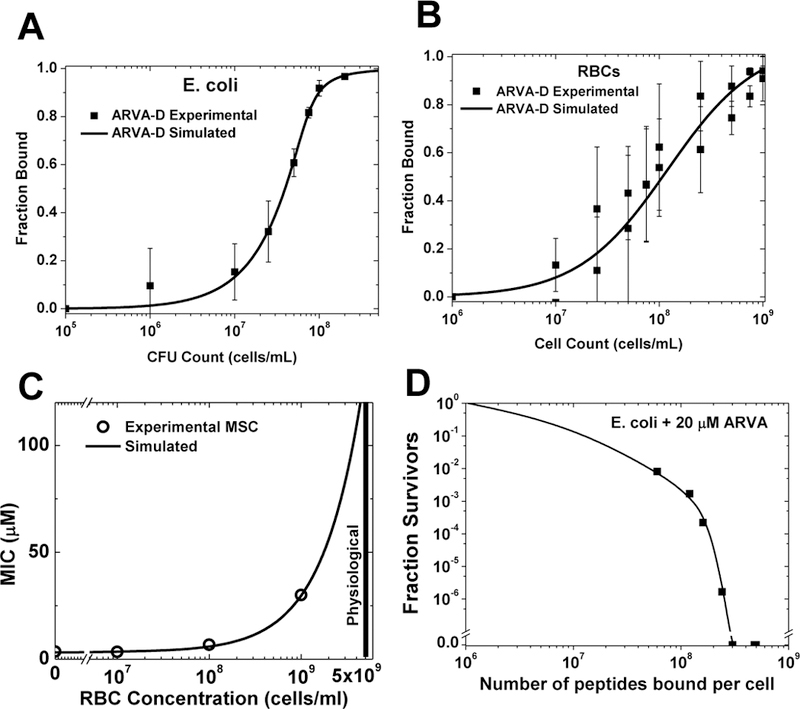
Saturation-dependent activity of an antimicrobial peptide and its inhibition by host cells. The protease resistant AMP D-ARVA (rrgwalrlvlay-NH2) was used in these experiments1–3. A: Measured binding of D-ARVA to E. coli cells. B: Measured binding of D-ARVA to human RBCs. C: Experimental measurements compared to simulation of a mixed experiment assuming simple competition between E. coli and RBC shows that the measured binding accounts for the loss of activity when host cells are present. D: Survival of different innocula of E. coli incubated with 20 μM D-ARVA in conjunction with the binding curve in panel A, enables comparison of peptide lethality and the number of peptides bound to each bacterial cell. More than 2×108 peptides bound per cell are required for sterility.
