Figure 4.
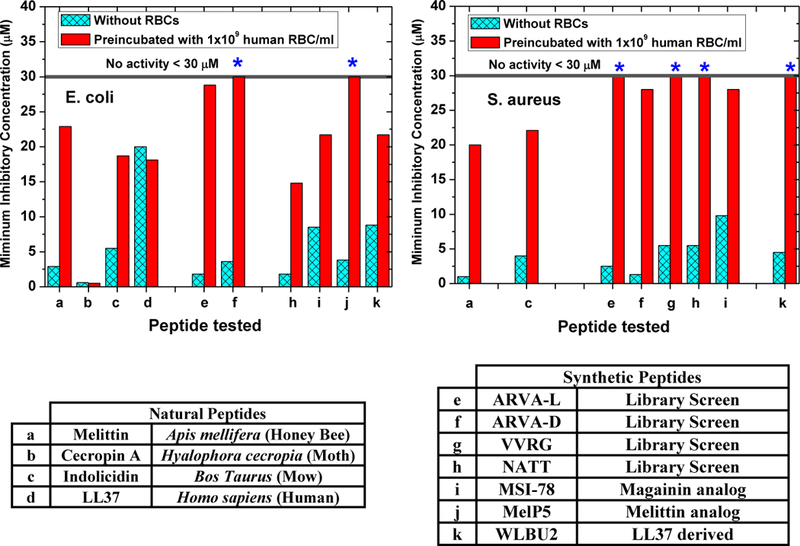
Human Red Blood cells inhibit antimicrobial peptides. As described elsewhere1 preincubation of natural and synthetic AMPs with 1×109 human RBC/ml (2% of physiological concentration) causes inhibition of most, but not all, of them. We have shown that such host cell inhibition is the result of direct RBC binding and also to proteolysis of the AMP by the cytosolic proteases found in human RBCs7.
