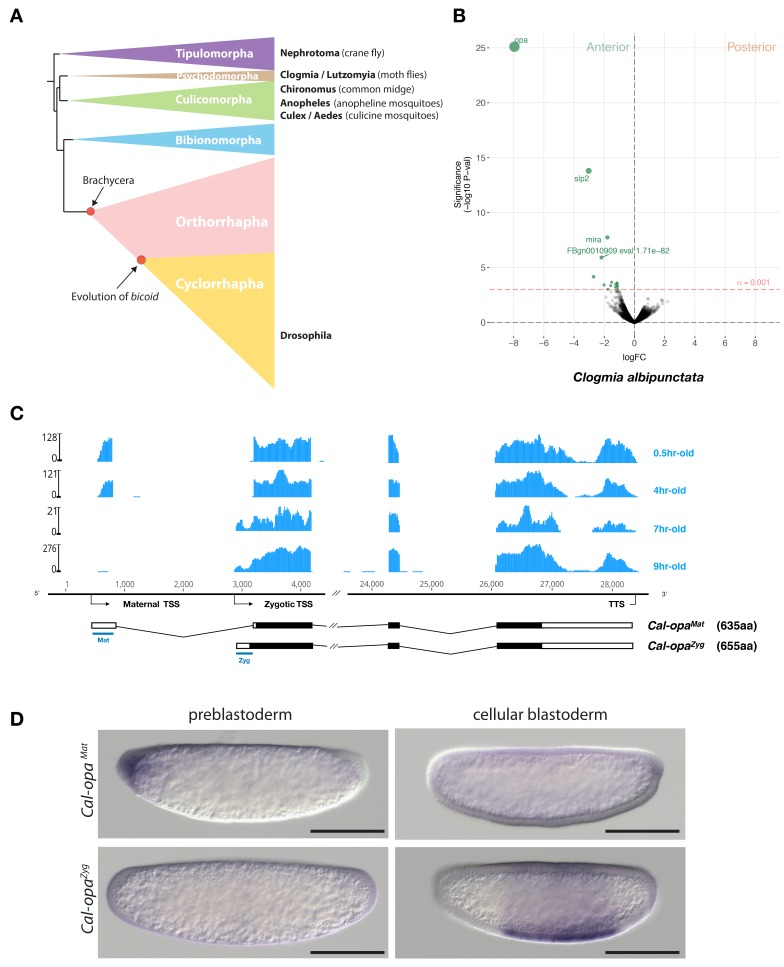
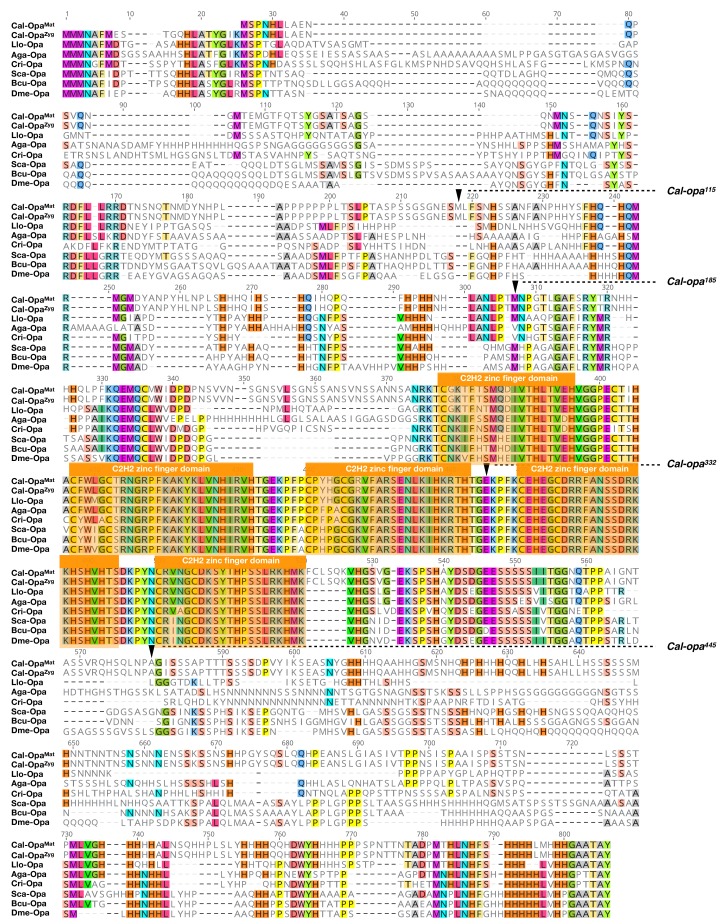
Figure 1. Expression of alternative Cal-opa transcripts in Clogmia embryos.
(A) Phylogenetic relationship of fly species referred to in the text (Wiegmann et al., 2011). (B) Differential expression analysis of maternal transcripts between anterior and posterior halves of 1 hr-old Clogmia embryos. logFC: log fold-change. (C) Stage-specific RNA-seq read coverage of Cal-opa locus. Transcription start sites (TSS) and transcription termination sites (TTS) are indicated on the genomic scaffold (solid line with 1000 bp intervals marked) and were confirmed by RACE. Exon-intron sketches of Cal-opaMat and Cal-opaZyg transcript variants are shown with the open reading frame in black and the position of in situ hybridization probes and dsRNA underlined in blue. (D) RNA in situ hybridization of Cal-opaMat and Cal-opaZyg transcripts in 1 hr-old preblastoderm and 7 hr-old cellular blastoderm embryos. Anterior is left and dorsal up. Scale bar: 100μm.