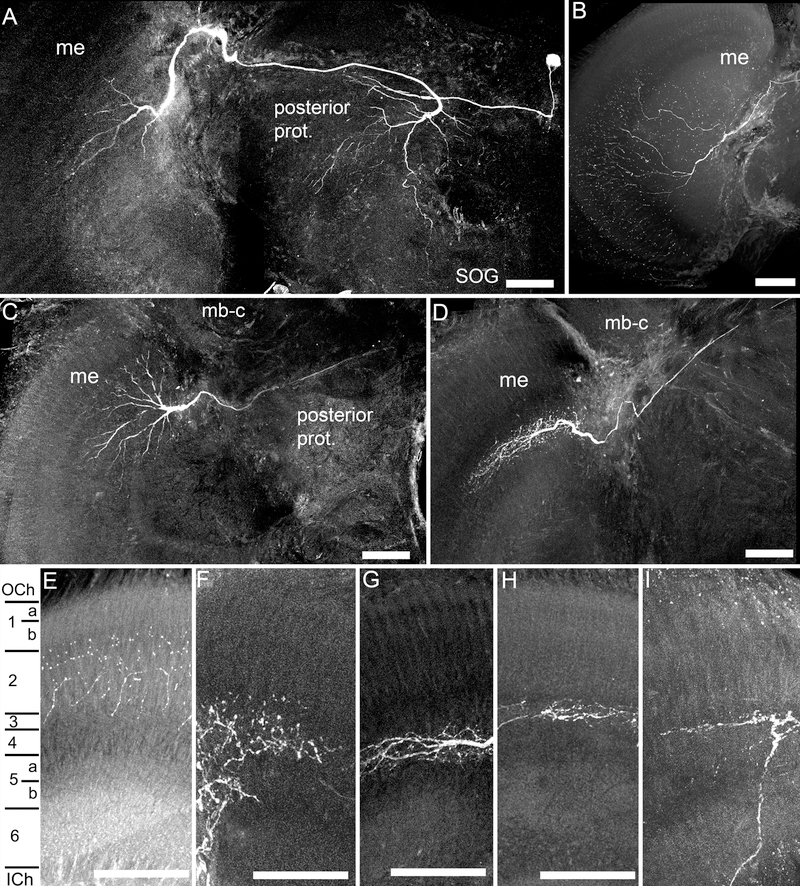
Fig. 2.
Anatomical characteristics of recorded medulla neurons. A. Frontal view of a large field medulla neuron, with branching in the dorsal medulla (me), and which projected posteriorly into the posterior protocerebrum (prot.), with a fine process toward the subesophageal ganglion (SOG). B. A large field medulla neuron, with branching throughout most of the medulla. C. A large field medulla neuron with branching in the dorsal medulla, and a faded projection across the brain in the posterior protocerebrum. D. A large field medulla neuron with branching patterns in the dorsal medulla. E-I. The fine branching patterns in the layers of the medulla, with different neurons entering either the outer medulla layers (E,F), or the inner medulla layers (G-I). E-G, large field medulla neurons; H,I, amacrine medulla neurons. Scale bars = 100 μm.