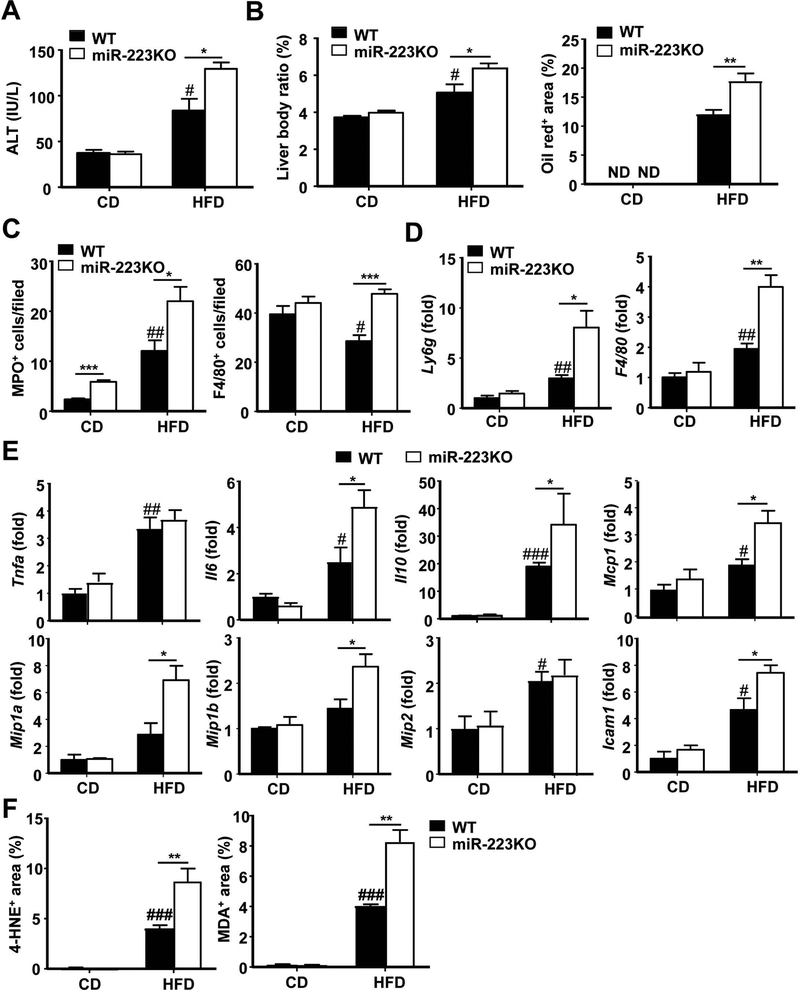
Figure 2. miR-223KO mice are more susceptible to 3m-HFD-induced liver injury, steatosis and inflammation.
WT and miR-223KO mice were fed an HFD or CD for three months. Serum and liver tissue samples were collected. (A) Serum ALT levels were measured. (B) Liver body ratio was measured. Lipids was stained with Oil Red and the quantitation of Oil Red+ area per field was determined. Representative images are shown in supporting Fig. S2D. (C) Liver tissues were also subjected to MPO and F4/80 immunostaining and the quantitation of MPO+ and F4/80+ cells per field was determined. Representative images are shown in Supporting Fig. S3A–B. (D, E) RT-qPCR analyses of liver Ly6g and F4/80 mRNA, and other inflammatory mediators. (F) Quantification of 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE)+ and malonaldehyde (MDA)+ area per field. Values represent means ± SEM (n=8–12). *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P<0.001 in comparison with corresponding WT groups; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 in comparison with WT CD group.