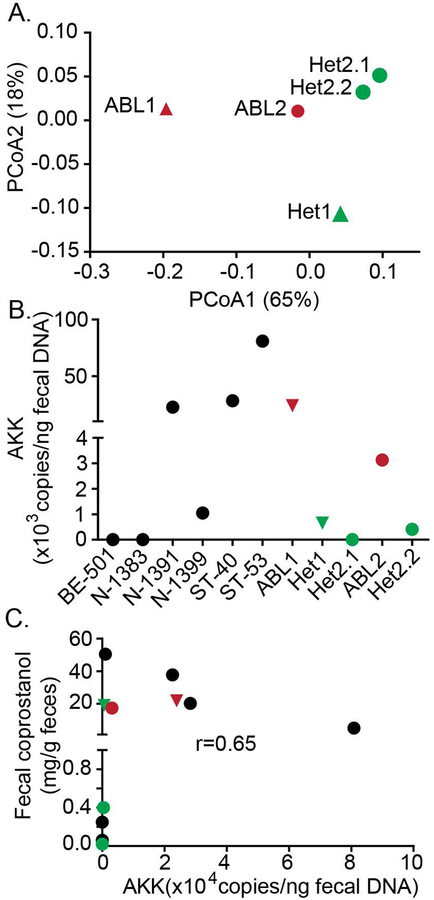
Figure 8. Fecal Akkermansia is enriched in Abetalipoproteinemia patients and its abundance is associated with fecal coprostanol in human subjects.
(A) Fecal DNA was extracted from 5 human subjects from two abetalipoproteinemia (ABL) families. Their gut bacterial communities were analyzed by Miseq 16S rRNA gene sequencing (Methods). ABL1 and Het1 were from ABL family 1 (solid triangles). ABL2, Het2.1 and Het2.2 were from ABL family 2 (solid circles). Weighted UniFrac distance was used for principle component analysis. Gut bacterial communities of ABL patients were clustered closer, distinct from their family members. Each dot represents a fecal community. (B) Akkermansia abundance in human fecal DNAs (including 6 samples from normal subjects) was determined by qPCR. (C) Fecal neutral sterol content was quantitated by GC (Supplemental Methods). Pearson-Spearman correlation analysis identified a positive correlation between Akkermansia abundance and host fecal coprostanol content (right). Red indicates ABL proband; green indicates the heterozygous family member; black indicates normal controls.